2012 Employer Health Benefits Survey
Section 8: High-Deductible Health Plans with Savings Option
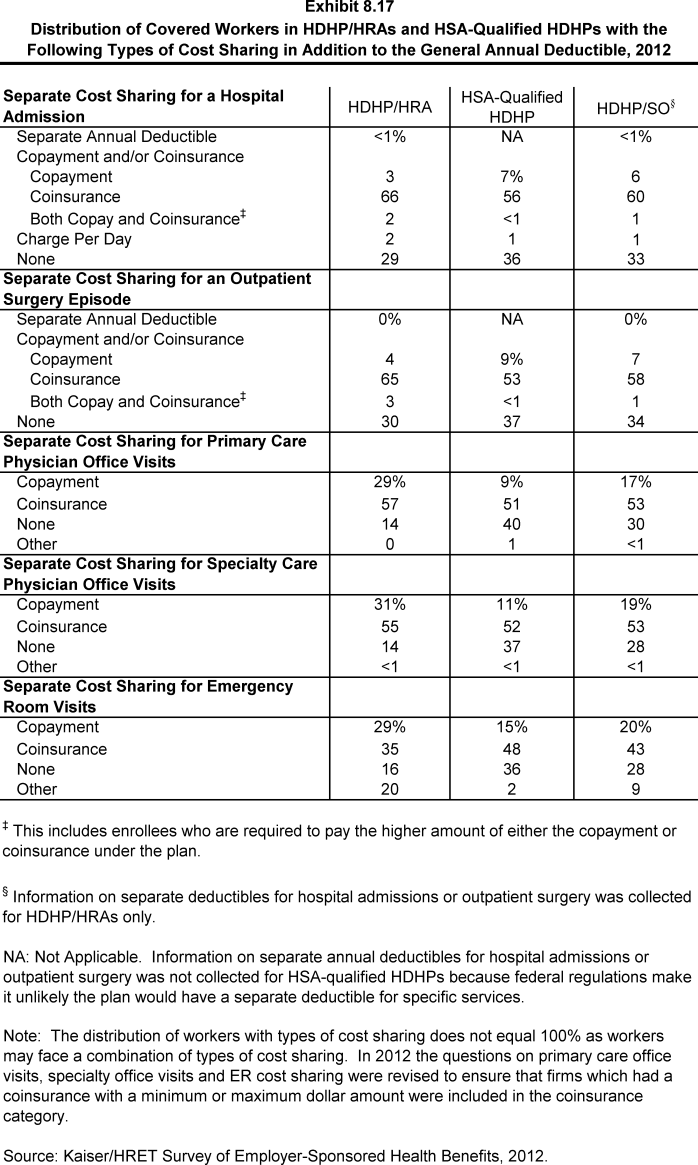
Changes in law over the past few years have permitted the establishment of new types of savings arrangements for health care. The two most common are health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs) and health savings accounts (HSAs). HRAs and HSAs are both financial accounts that workers or their family members can use to pay for health care services. These savings arrangements are often (or, in the case of HSAs, always) paired with health plans with high deductibles. The survey treats high-deductible plans that can be paired with a savings option as a distinct plan type – High-Deductible Health Plan with Savings Option (HDHP/SO) – even if the plan would otherwise be considered a PPO, HMO, POS plan, or conventional health plan. Specifically for the survey, HDHP/SOs are defined as (1) health plans with a deductible of at least $1,000 for single coverage and $2,000 for family coverage1 offered with an HRA (referred to as HDHP/HRAs); or (2) high-deductible health plans that meet the federal legal requirements to permit an enrollee to establish and contribute to an HSA (referred to as HSA-qualified HDHPs).2
Percentage of Firms Offering HDHP/HRAs and HSA-Qualified HDHPs, and Enrollment
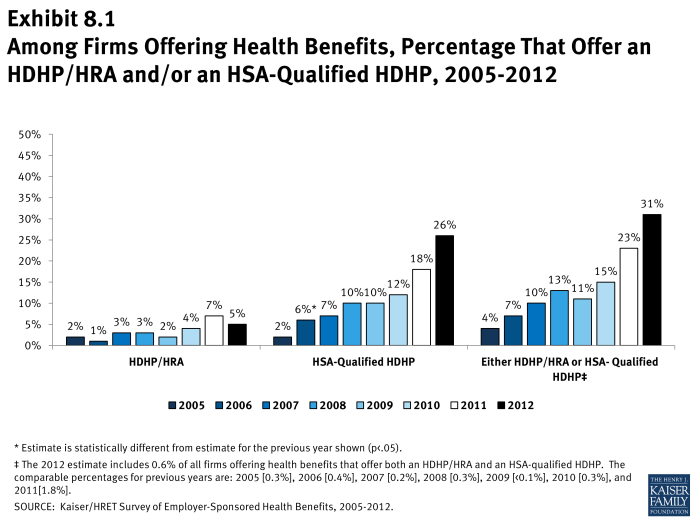
- Thirty-one percent of firms offering health benefits offer an HDHP/HRA or an HSA-qualified HDHP. Among firms offering health benefits, 5% offer an HDHP/HRA and 26% offer an HSA-qualified HDHP (Exhibit 8.1).
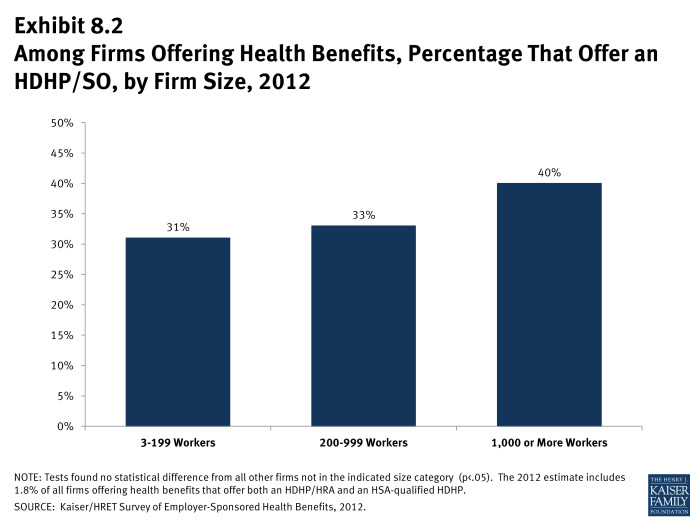
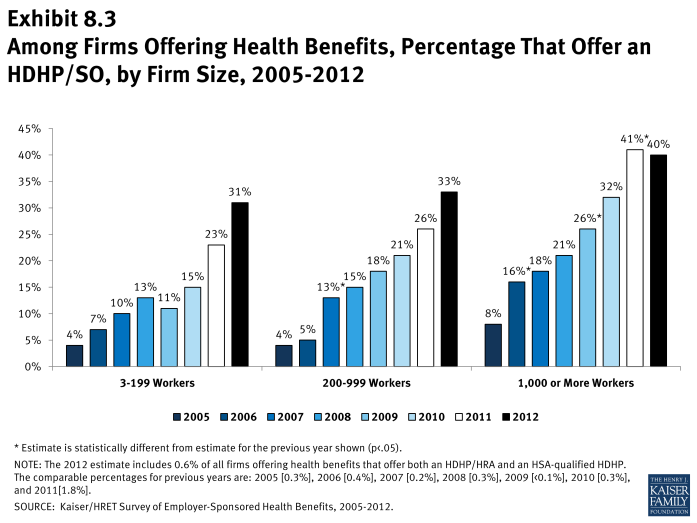
- Firms with 5,000 or more workers are significantly more likely to offer an HDHP/SO than smaller firms. Forty-eight percent of firms with 5,000 or more workers offer an HDHP/SO, compared to 31% of firms with 3 to 199 workers, 33% of firms with 200-999 workers, or 38% of firms with 1,000 to 4,999 workers (Exhibit 8.2).
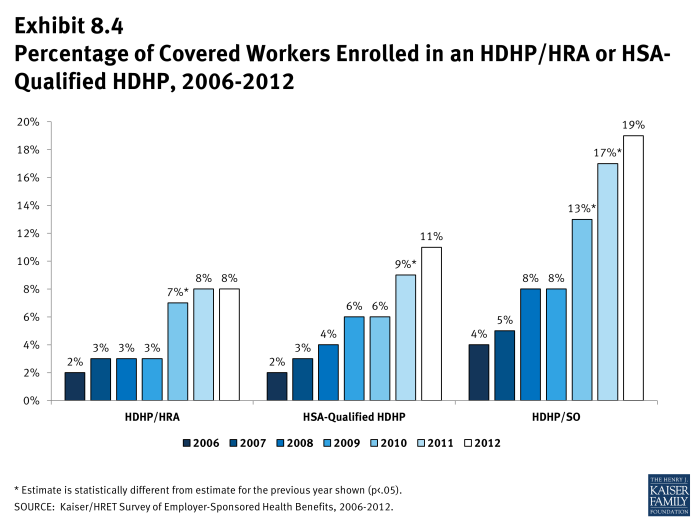
- Nineteen percent of covered workers are enrolled in an HDHP/SO in 2012, similar to the 17% enrolled last year (Exhibit 8.4). Enrollment in HDHP/SOs had increased significantly in previous years (13% in 2010; 8% in 2009).
- Eight percent of covered workers are enrolled in HDHP/HRAs in 2012, and 11% percent of covered workers are enrolled in HSA-qualified HDHPs (Exhibit 8.4).
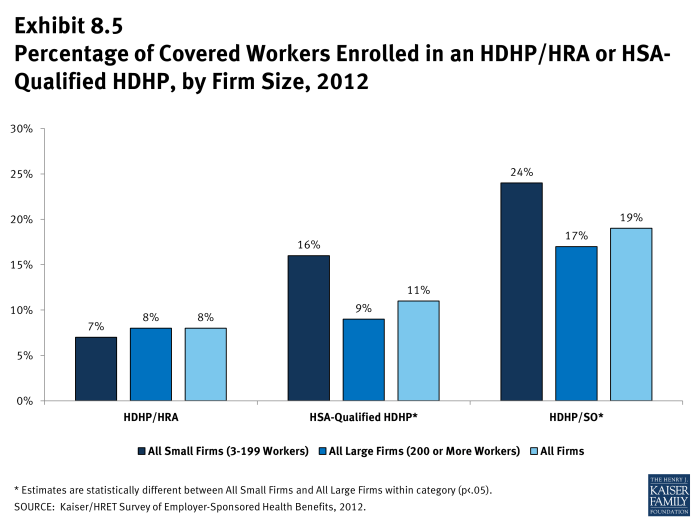
- Twenty-four percent of covered workers in small firms (3-199 workers) are enrolled in HDHP/SOs, compared to 17% of workers in large firms (200 or more workers) (Exhibit 8.5).
- The percentage of workers in small firms (3-199 workers) enrolled in HSA-qualified HDHP/SOs is higher than the percentage of workers in large firms enrolled in HSA-qualified HDHP/SOs (16% vs. 9%) (Exhibit 8.5).
Plan Deductibles
- As expected, workers enrolled in HDHP/SOs have higher deductibles than workers enrolled in HMOs, PPOs, or POS plans.
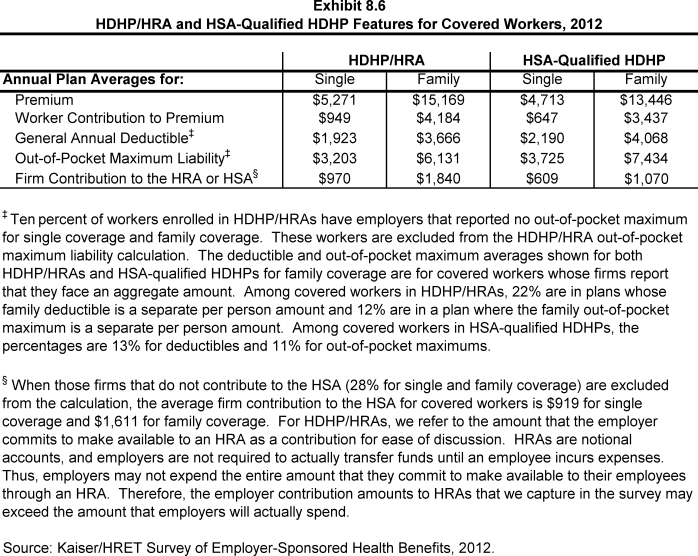
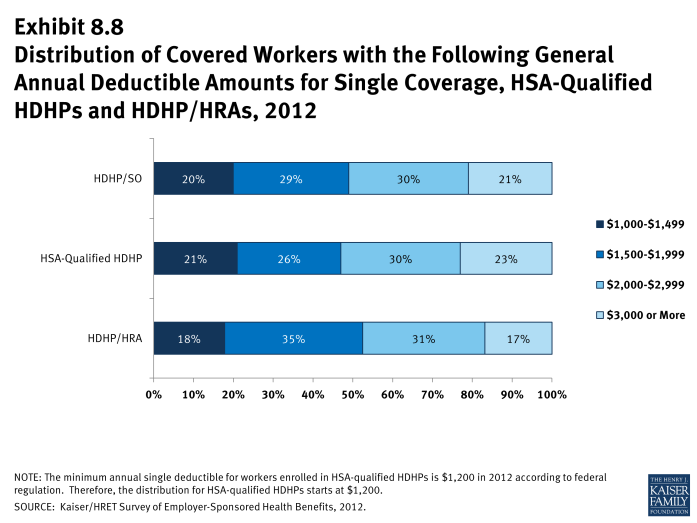
- The average general annual deductible for single coverage is $1,923 for HDHP/HRAs and $2,190 for HSA-qualified HDHPs (Exhibit 8.6). These averages are similar to the amounts reported in recent years. There is wide variation around these averages (Exhibit 8.8).
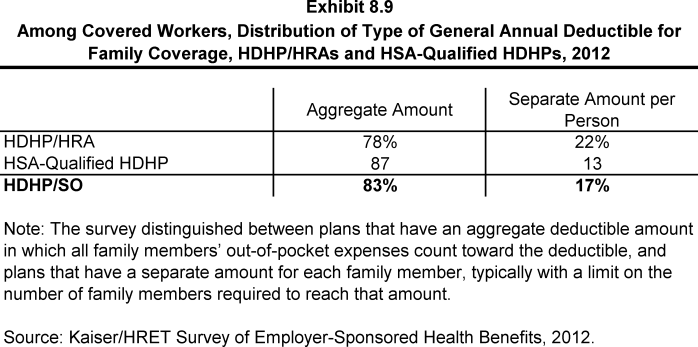
- Since 2006, the survey has collected information on two types of family deductibles. The survey asks employers whether the family deductible amount is (1) an aggregate amount (i.e., the out-of-pocket expenses of all family members are counted until the deductible is satisfied), or (2) a per-person amount that applies to each family member (typically with a limit on the number of family members that would be required to meet the deductible amount).
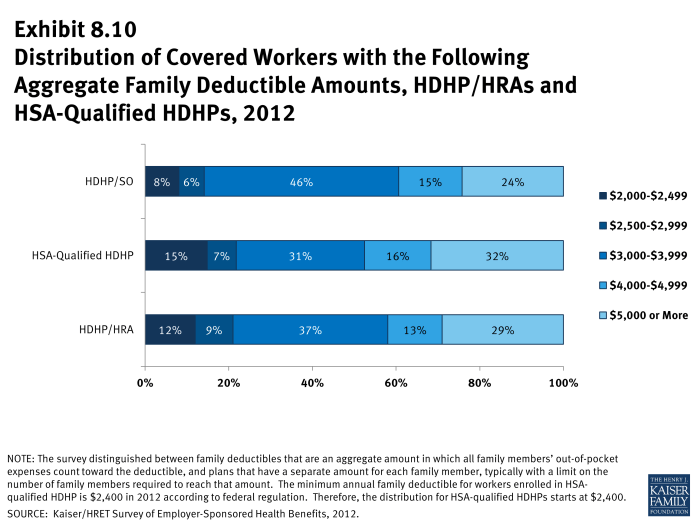
- The average aggregate deductibles for workers with family coverage are $3,666 for HDHP/HRAs and $4,068 for HSA-qualified HDHPs (Exhibit 8.6). There is wide variation around these average amounts for family coverage (Exhibit 8.10).
Out-of-Pocket Maximum Amounts
- HSA-qualified HDHPs are legally required to have a maximum annual out-of-pocket liability of no more than $6,050 for single coverage and $12,100 for family coverage in 2012. HDHP/HRAs have no similar requirement.
- The average annual out-of-pocket maximum for single coverage is $3,203 for HDHP/HRA4 and $3,725 for HSA-qualified HDHPs (Exhibit 8.6).
- As with deductibles, the survey asks employers whether the family out-of-pocket maximum liability is (1) an aggregate amount that applies to spending by any covered person in the family, or (2) a separate per person amount that applies to spending by each family member or a limited number of family members. The survey also asks whether spending by enrollees on various services counts towards meeting the plan out-of-pocket maximum.
- Among covered workers with family coverage whose out-of-pocket maximum is an aggregate amount that applies to spending by any covered person in the family, the average annual out-of-pocket maximums are $6,131 for HDHP/HRAs and $7,434 for HSA-qualified HDHPs (Exhibit 8.6).
Premiums
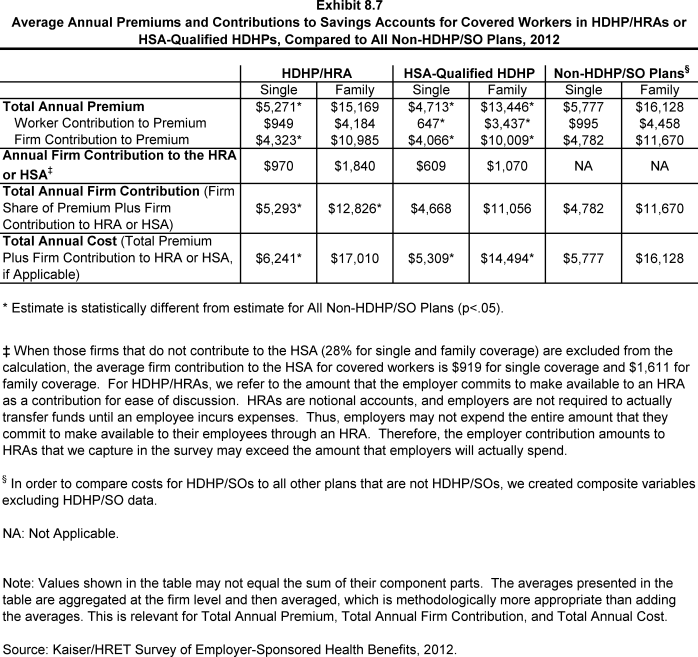
- In 2012, the average annual premiums for HDHP/HRAs are $5,271 for single coverage and $15,169 for family coverage. For single coverage, the HDHP/HRA average premium for covered workers is significantly lower than the average premium for covered workers in plans that are not HDHP/SOs (Exhibit 8.7).
- The average annual premium for workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs is $4,713 for single coverage and $13,446 for family coverage. These amounts are lower than the average single and family premium for workers in plans that are not HDHP/SOs (Exhibit 8.7).
Worker Contributions to Premiums
- The average annual worker contributions to premiums for workers enrolled in HDHP/HRAs are $949 for single coverage and $4,184 for family coverage (Exhibit 8.6).
- The average annual worker contributions to premiums for workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs are $647 for single coverage and $3,437 for family coverage (Exhibit 8.6).
The average contribution for single coverage for workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs is significantly less than the average premium contribution made by covered workers in plans that are not HDHP/SOs (Exhibit 8.7).
Employer Contributions to Premiums and Savings Options
- Employers contribute to HDHP/SOs in two ways: through their contributions toward the premium for the health plan and through their contributions (if any, in the case of HSAs) to the savings account option (i.e., the HRAs or HSAs themselves).
- Looking just at the annual employer contributions to premiums, covered workers in HDHP/HRAs on average receive employer contributions of $4,323 for single coverage and $10,985 for family coverage. The average employer contribution for single coverage in HDHP/HRAs is significantly less than the average employer premium contribution for plans that are not HDHP/SOs. (Exhibit 8.7).
- The average annual employer contributions to premiums for workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs are $4,066 for single coverage and $10,009 for family coverage. These amounts are lower than the average contributions for single or family coverage for workers in plans that are not HDHP/SOs (Exhibit 8.7).
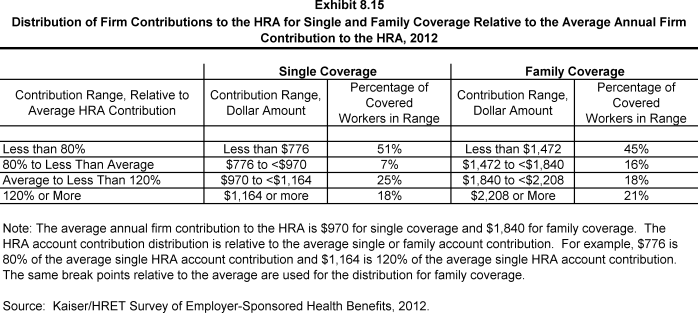
- When looking at employer contributions to the savings option, workers enrolled in HDHP/HRAs receive, on average, an annual employer contribution to their HRA of $970 for single coverage and $1,840 for family coverage (Exhibit 8.7).
- HRAs are generally structured in such a way that employers may not actually spend the whole amount that they make available to their employees’ HRAs.5 Amounts committed to an employee’s HRA that are not used by the employee generally roll over and can be used in future years, but any balance may revert back to the employer if the employee leaves his or her job. Thus, the employer contribution amounts to HRAs that we capture in the survey may exceed the amount that employers will actually spend.
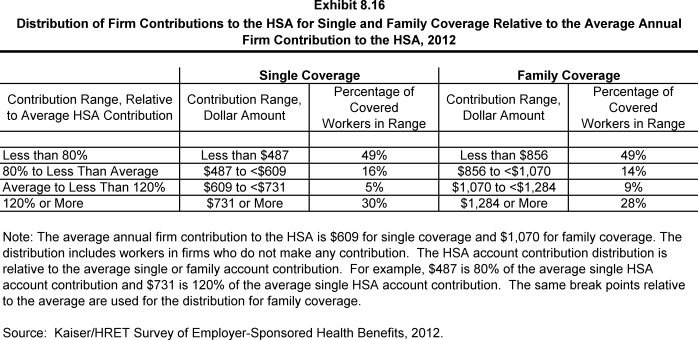
- Workers enrolled in HSA-qualified HDHPs on average receive an annual employer contribution to their HSA of $609 for single coverage and $1,070 for family coverage (Exhibit 8.7).
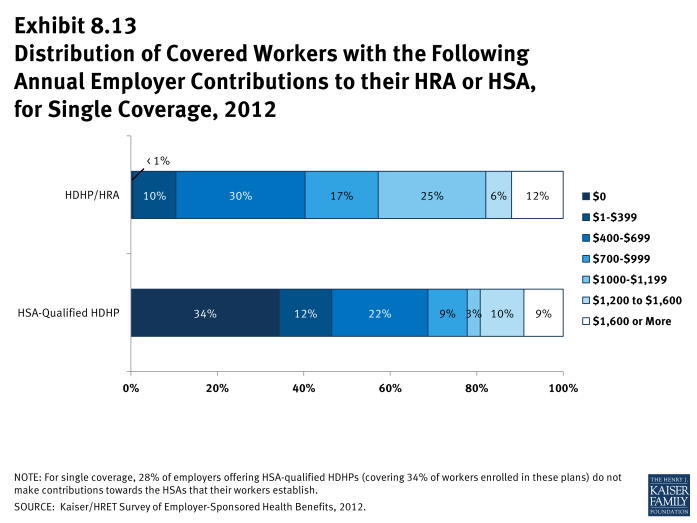
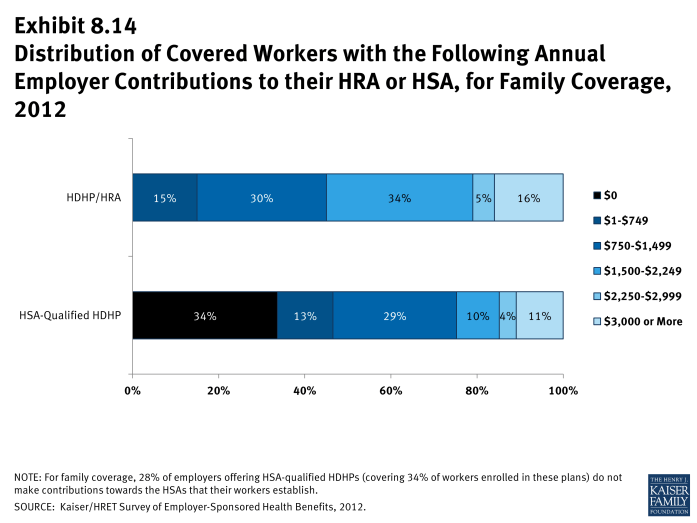
- In some cases, employers that sponsor HSA-qualified HDHP/SOs do not make contributions to HSAs established by their employees. Twenty-eight percent of employers offering single and family coverage through HSA-qualified HDHPs do not make contributions towards the HSAs that their workers establish (Exhibit 8.7). Thirty-four percent of workers with single or family coverage in an HSA-qualified HDHP do not receive an account contribution from their employer (Exhibit 8.13) and (Exhibit 8.14).
- The average HSA contributions reported above include the portion of covered workers whose employer contribution to the HSA is zero. When those firms that do not contribute to the HSA are excluded from the calculation, the average employer contribution for covered workers is $919 for single coverage and $1,611 for family coverage (Exhibit 8.7).
- Employer contributions to savings account options (i.e., the HRAs and HSAs themselves) for their employees can be added to their health plan premium contributions to calculate total employer contributions toward HDHP/SOs.
- For HDHP/HRAs, the average annual total employer contribution for covered workers is $5,293 for single coverage and $12,826 for family coverage. The average total employer contribution amounts for single and family coverage in HDHP/HRAs are higher than the average amount that employers contribute towards single and family coverage in health plans that are not HDHP/SOs (Exhibit 8.7).
- For HSA-qualified HDHPs, the average annual total employer contribution for covered workers is $4,668 for single coverage and $11,056 for workers with family coverage. The total amounts contributed for workers in HSA-qualified HDHPs for single and family coverage are similar to the amounts contributed for workers not in HDHP/SOs (Exhibit 8.7).