Back to School amidst the New Normal: Ongoing Effects of the Coronavirus Pandemic on Children’s Health and Well-Being
As millions of children across the nation prepare to go back to school this fall, many will face challenges due to ongoing health, economic, and social consequences of the pandemic. Children may be uniquely impacted by the pandemic, having experienced this crisis during important periods of physical, social, and emotional development, and some have experienced the loss of loved ones. Further, households with children have been particularly hard hit by loss of income, food and housing insecurity, and disruptions in health care coverage, which all affect health and well-being. Public health measures to reduce the spread of the disease also led to disruptions or changes in service utilization, difficulty accessing care, and increased mental health challenges for children. Young children are still not eligible for vaccination, and though children are likely to be asymptomatic or experience only mild symptoms, they can contract COVID-19. Children may face new risks due to the rapid spread of the Delta variant, and some children who contract COVID-19 experience long-term effects from the disease. Many of these effects have disproportionately affected low-income children and children of color, who faced increased health and economic challenges even prior to the pandemic. This brief examines how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected the health and well-being of children, explores recent policy responses, and considers what the findings means for the back-to-school season amidst new challenges due to the recent increase in cases and deaths. Key findings include:
- During the pandemic, some children experienced disruptions in routine vaccinations or preventive care appointments and difficultly accessing care, particularly dental and specialized care. Use of telemedicine has increased but not enough to offset declines in service utilization overall.
- Children’s mental health service utilization declined amid elevated symptoms of depression, anxiety, and psychological stress for children and parents.
- Households with children have experienced significantly higher rates of economic hardships throughout the pandemic compared to households without children, leading to increased barriers to adequately addressing social determinants of health. Black, Hispanic, and other people of color have been disproportionately impacted by the pandemic’s economic effects.
- Though the risk of severe illness from COVID-19 is lower for children than adults, over 43,000 children are estimated to have lost a parent due to COVID-19, with Black children being disproportionately impacted by parent death.
- Most children are likely to be back in the classroom this fall, but many still face health risks due to their or their teachers’ vaccination status. Some states and school districts are beginning to announce mask or vaccine requirements while others are banning vaccine or mask mandates for schools.
Recent policy developments, most notably the American Rescue Plan Act and the American Families Plan, attempt to alleviate some of the existing and pandemic-induced issues impacting children’s health and well-being. However, there is still uncertainty around what back to school will look like this fall, and the transition to “the new normal” may be more difficult for some. Schools, parents, and policymakers may face additional pressure to address the ongoing effects of the pandemic on children.
Children’s Health Care Disruptions and Mental Health Challenges
The pandemic has led to delays in child vaccinations and preventive care. KFF analysis of the Household Pulse Survey from June 23 – July 5, 2021 estimates 25% of households with children have a child who has missed, delayed, or skipped a preventive appointment in the past 12 months due to the pandemic (Figure 1). Preliminary Medicaid administrative data confirms this pattern, showing that when comparing March 2020 – October 2020 to the same months before the pandemic in 2019, there were approximately 9% fewer vaccinations for children under 2 and 21% fewer child screening services. Rates for primary and preventative care among Medicaid beneficiaries show signs of rebounding in more recent months with service use reflecting pent-up demand, but it is unclear whether this trend will continue and make up for the millions of services missed early in the pandemic. Another recent study similarly reports vaccinations for all children declined sharply after March 2020. The study also finds vaccinations have completely recovered for children under 2 but have only partially recovered for older children.
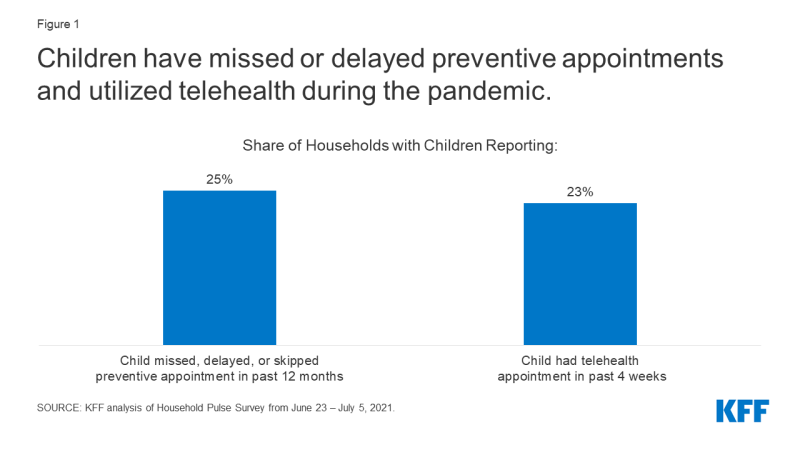
Figure 1: Children have missed or delayed preventive appointments and utilized telehealth during the pandemic
Children also experienced difficulty accessing and disruptions in specialty and dental care. Parents have reported delaying dental care or difficulty accessing dental care for their child, and there were 39% fewer dental services for Medicaid/CHIP beneficiaries under 19 when comparing the pandemic months March 2020 – October 2020 to the same months in 2019. Children with special health care needs experienced difficulties accessing specialized services, especially services that could not be conducted via telehealth.
Children’s utilization of telemedicine services has increased since the pandemic, but the increase has not offset the decreases in service utilization overall. Preliminary data suggest that telehealth utilization for Medicaid/CHIP beneficiaries under 19 increased rapidly in April 2020 and remains higher than before the pandemic. 23% of households with children surveyed by the Household Pulse Survey from June 23 – July 5, 2021 reported a child having a telehealth appointment in the past 4 weeks (Figure 1). Throughout the pandemic, the federal government and states have taken action to expand access to telehealth services. While telehealth utilization has increased, the increase has not offset the decreases in service utilization overall, and barriers to accessing health care via telehealth may remain, especially for low-income patients or patients in rural areas.
Children’s mental health and mental health service utilization has worsened since the start of the pandemic. The pandemic caused disruptions in routines and social isolation for children, which can be associated with anxiety and depression and can have implications for mental health later in life. Also, research has shown that as economic conditions worsen, children’s mental health is negatively impacted. Parents with young children reported in October and November of 2020 that their children showed elevated symptoms of depression, anxiety, and psychological stress and 22% experienced overall worsened mental or emotional health. Recent studies by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) find children’s emergency department visits increased during the pandemic for mental health-related emergencies and suspected suicide attempts by children ages 12 to 17. At the same time, mental health service utilization has declined, with preliminary data for Medicaid/CHIP beneficiaries suggesting there have been approximately 34% fewer mental health services when comparing the pandemic months March 2020 – October 2020 to the same months in 2019. Private mental health care claims also decreased from 2019 to 2020. There has been an increase in access to mental health care through telehealth, but there remain technological and privacy barriers to accessing mental health services via telehealth for some children.
Parental stress and poor mental health due to the pandemic can negatively affect children’s health. A previous KFF analysis finds economic uncertainty has led to increased mental health challenges, especially for adults in households with children and specifically mothers in those households. Further, 46% of mothers who reported a negative mental health impact due to the pandemic were not able to access needed mental health. Parental stress can negatively affect children’s emotional and mental health, harm the parent-child bond, and have long-term behavioral implications. Maternal depression can worsen child health status and lead to less preventative care. Additionally, parental stress and financial hardship can lead to an increased risk of child abuse and neglect. Early evidence shows declines in child abuse during the pandemic, though it is unclear if that is due to decreased reporting or due to social policy interventions during the pandemic. Children’s existing and pandemic-induced mental health challenges may have implications for the transition back to school and indicate children may need additional mental health support when they return to school.
Pandemic-related challenges in children’s access to health care built on a system that was sometimes not meeting needs even before the pandemic, especially for low-income children. In 2019, 23% of children living in households with incomes below 100% of the federal poverty level (FPL) were estimated to have not received a preventative check-up in the past 12 months and 26% did not see a dentist for a preventive visit during the past 12 months (Figure 2). Some children with mental health needs were not receiving care, with an estimated 29% of the lowest income children who needed mental health services not able to access care (Figure 2). The pandemic may have made it even more challenging for children already experiencing difficulties accessing care and likely worsened existing disparities in access to needed care for children of color, children with special health care needs, children in low-income households, and children living in rural areas.
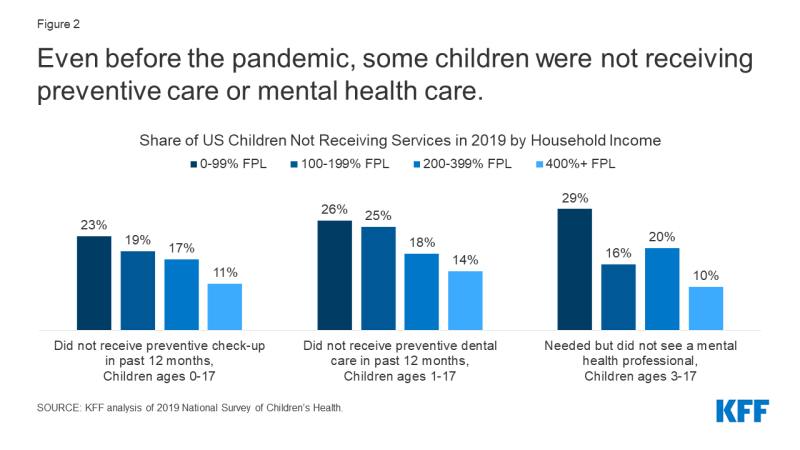
Figure 2: Even before the pandemic, some children were not receiving preventive care or mental health care
The Economic Downturn and Children’s Well Being
Following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, many families with children were faced with unemployment and income loss and continue to face economic hardship. Throughout the pandemic, households with children were consistently more likely to report job or income loss, with more than half of households with children reporting losing income between March 2020 and March 2021.1 While national indicators signaling job and income loss have moderated in recent months, they are still not at pre-pandemic levels. KFF analysis of the Census Bureau’s Household Pulse Survey from June 23 – July 5, 2021 found 12% of adults with children in the household applied for Unemployment Insurance (UI) benefits and 23% experienced loss of income in the past 4 weeks (Figure 3). These rates were significantly higher compared to adults without children in the household.
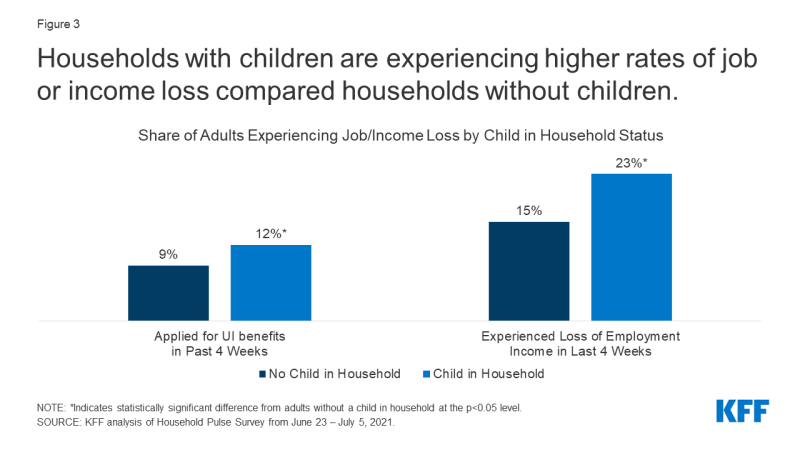
Figure 3: Households with children are experiencing higher rates of job or income loss compared households without children
Loss of family income affects parents’ ability to provide for children’s basic needs. KFF analysis of the Census Bureau’s Household Pulse Survey also found that among adults reporting income loss in the past 4 weeks, 91% of adults with children in the household reported difficultly paying for expenses in the past week, 20% reported not having confidence in their ability to make their next month’s housing payment, and 32% reported food insufficiency (Figure 4). All of these rates are significantly higher for adults living in households with children than adults living in households without children. A large body of research shows that economic instability is a social determinant of health outcomes for children.
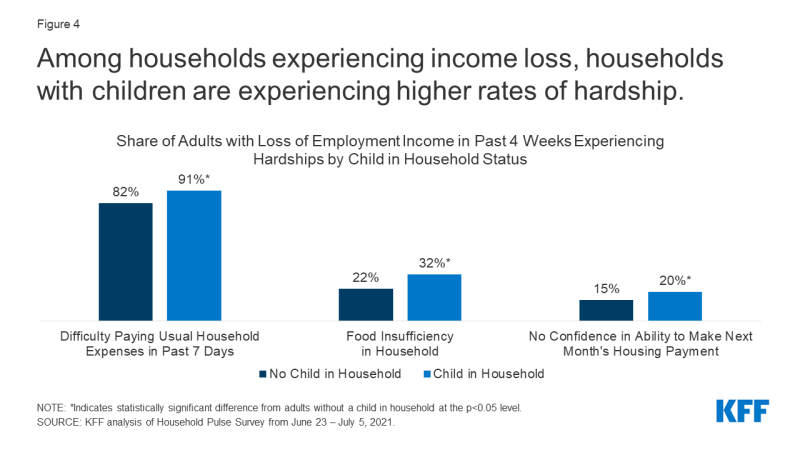
Figure 4: Among households experiencing income loss, households with children are experiencing higher rates of hardship
Further, Black, Hispanic,2 and other households of color have been disproportionately impacted by the pandemic and its economic effects. In 2019, Black and Hispanic children were nearly three times more likely to be living in poverty than Asian and White children, and food insufficiency rates before the pandemic were three times higher for Black households and two time higher for Hispanic households when compared to White households. A recent report found Hispanic and Black households with children have experienced almost double the rate of economic or health-related hardships during the pandemic compared to White and Asian households with children. Overall, child poverty rates children have increased during the pandemic, especially among Hispanic and Black children.
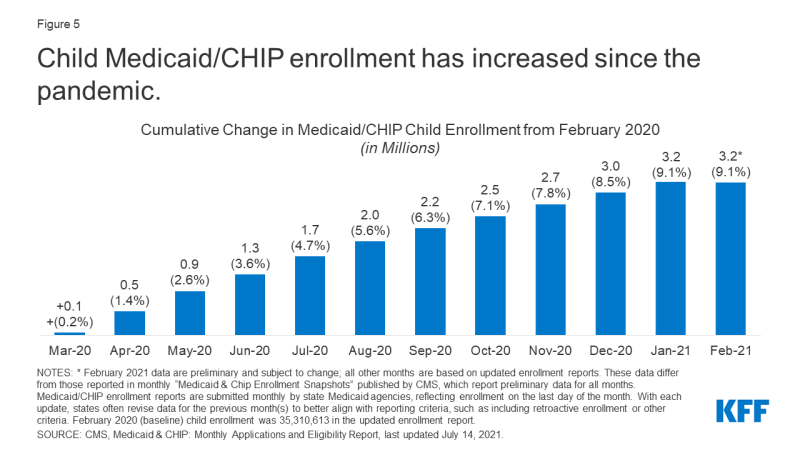
Job and income loss may lead to disruptions in children’s health coverage, though increased coverage through Medicaid and CHIP is likely offsetting much of that decline. Roughly 2 to 3 million people between March and September 2020 have lost employer health benefits, a trend that built on years of coverage losses among children. From 2016 and 2019, the rate of uninsured children in the US started to increase despite reaching the lowest rate in history (4.7%) in 2016, with the rate of uninsured Hispanic children increasing more than twice as fast as the rate for non-Hispanic youth. Loss of coverage or coverage interruptions can negatively impact children’s ability to access needed care.3,4,5 During the pandemic, Medicaid and CHIP provided a safety net for many children. Administrative data for Medicaid show that children’s enrollment in Medicaid and CHIP has increased between February 2020 and February 2021, a total increase of 3.2 million enrollees, or 9.1%, from child enrollment in February 2020 (Figure 5).
Children’s Health and COVID-19
While likely to be asymptomatic or experience only mild symptoms, children can contract COVID-19. Preliminary data through July 29, 2021 show there have been over 4 million child COVID-19 cases, and children with underlying health conditions may be at an increased risk of developing severe illness. Though a small percentage, some children who tested positive for the virus are now facing long haul symptoms, with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) the most-common complication that has impacted 4,000 children as of June 2, 2021. It is unclear how long symptoms will last and what impact they will have on children’s long-term health. Cases have risen in recent weeks due to the Delta variant, and children are making up an increasing share of new cases, with children making up 19.0% of cases for the week ending in July 29 compared to 14.3% since the pandemic began. Hospitalizations of children with COVID-19 have also been rising since early July, reaching 216 children, on average, being admitted to the hospital every day for the week of July 31 – August 6, 2021.
Eligible children have lower vaccination rates than the adult population, and some children remain ineligible for a vaccine. Children 12 and up are now able to be vaccinated against COVID-19, which reduces the risk of adolescents contracting, spreading, or experiencing severe symptoms from COVID-19. Approximately 37% of children ages 12-15 and 48% of children ages 16-17 have received at least one vaccine dose as of July 26, 2021. These rates are lower than the adult population, which reached 70% as of August 2, 2021. There is currently no COVID vaccine for children under the age of 12, so some risk remains for that population to contract and spread the virus. Vaccine clinical trials are currently underway for children under 12, with authorization expected by the end of 2021. The KFF COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor recently reported that almost half of parents of children ages 12-17 say their child has received a COVID-19 vaccine or they intend to get them vaccinated right away. The report also found that parents’ vaccination intentions for their children are largely correlated with their own vaccination status and those who say their child’s school provided information on or encouraged COVID-19 vaccines are more likely to report their child has received a vaccine. The KFF COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor also found that parents are more cautious when it comes to vaccinating their child under 12, with about a quarter saying they would get their child between the ages of 5 and 11 vaccinated right away once the vaccine is authorized and four in ten saying they would wait and see.
Some children have experienced COVID-19 through the loss of one or more family members due to the virus. A study estimates that, as of Feb. 2021, 43,000 children in US have lost at least one parent to COVID-19. The study also finds Black children represent only 14% of children in the US but 20% of children who have lost a parent, and low-income communities and communities of color overall experienced higher COVID-19 case rates and deaths. Losing a parent can have long term impacts on a child’s health, increasing their risk of substance abuse, mental health challenges, poor educational outcomes, and early death. Further, the death of a loved one from COVID-19 may have occurred amid increased social isolation and economic hardship due to the pandemic. Estimates indicate a 17.5% to 20% increase in bereaved children due to COVID-19, indicating an increased number of grieving children who may need additional supports as they head back to school in the fall.
Policy Responses
Several policies passed during the pandemic provided financial relief for families with children. To address the economic fallout of the pandemic, the federal government passed relief bills that included direct financial relief for families, and evidence suggests material hardships that affect health, such as food insufficiency and financial instability, declined following stimulus payments. In addition, the March 2021 American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) included targeted aid to families with children through the Child Tax Credit (CTC). The ARPA is projected to decrease the number of children living in poverty by over 40%, with the expanded CTC now reaching children previously too poor to qualify and giving families in the lowest quintile an average income boost of $4,470. Alleviating child poverty is associated with improved child health outcomes such as healthier birthweights, lower maternal stress, better nutrition, and lower use of drugs and alcohol.
Other recent policies directly target children’s health coverage or access to health care. To address health care coverage, the ARPA extended eligibility to ACA health insurance subsides for people with incomes over 400% of poverty and increased the amount of assistance for people with lower incomes. The ARPA also included incentives for states to expand Medicaid for low-income adults under the ACA and extend Medicaid postpartum coverage for up to 12 months, both of which could benefit the health and well-being of families.6,7 The Child Tax Credit, expanded by the ARPA, is not taxable income, so expanding the tax credit will not count toward Medicaid eligibility. To address access to health care challenges, the federal government and many states are making policy changes to permanently expand access to telehealth services. In their most recent report to congress, the Medicaid and CHIP Payment and Access Commission (MACPAC) recommended more coordinated efforts by agencies to address the design and implementation of benefits and improve access to home and community-based behavioral health services for Medicaid/CHIP children with significant mental health needs. In addition, the Biden Administration created a program to provide relief for COVID-19 related funeral costs, but targeted services for bereaved children were not included.
Back to School
Most children are likely to be back in the classroom this fall, but many still face health risks due to their or their teachers’ vaccination status and increasing transmission due to the Delta variant. The vast majority of schools, 88% of schools with 4th grade and 89% of schools with 8th grade, in the U.S. offered hybrid or full-time, in-person learning in Spring 2021, according to a federal survey. Most of these schools, as well as others, are likely to be in-person in fall 2021. While many states allow for in-person learning decision to be made at the local level, nine states have mandated schools return to in-person learning for the 2021-22 school year as of June 2021. No states are requiring the COVID-19 vaccine for school attendance at this time, and some states have enacted legislation to ban vaccine mandates for school attendance. However, due to concerns over the Delta variant and rising cases, some local districts are beginning to require the COVID-19 vaccine for teachers and staff. There have been legal challenges to vaccine mandates, with a federal District Court in Texas recently upholding a Hospital’s mandatory COVID-19 vaccination policy for employees. The CDC recently updated their guidance for COVID-19 in schools, recommending masks for all staff and students regardless of vaccination status for in-person learning in the fall. While some states and school districts will require students and staff to wear masks at school, at least nine states have passed legislation to ban mask mandates for schools as of late July 2021. Recent KFF polling shows that about half the public overall supports K-12 schools requiring COVID-19 vaccination, but most parents are opposed, with divisions along partisan lines.
While returning to in-person learning can support children’s development and well-being, the transition back to school in the fall may be challenging for some children. Experts notes that in-person learning is beneficial for children’s social, emotional, and physical health and can provide access to important health services and address racial and social inequities. However, this school year will look different for many children due to COVID-19 prevention strategies and transitioning back to “the new normal” may be difficult for some, especially those who have adapted to new routines and virtual learning in the past year. Children’s mental health has worsened during the pandemic, which could make the transition back to school more challenging. Additionally, young children who have been home with parents during the pandemic may experience separation anxiety as they transition back to school or day care.
Schools and proposed policies may provide additional supports for children and families as they transition back to school. The increased Child Tax Credits began July 15th and will continue monthly, but the enhanced CTC was only adopted for 2021. The American Families Plan put forth by the White House proposes to extend the CTC expansion through 2025 and make the credit permanently available to families with no earnings. The American Families Plan also proposes expanding school meals and access to healthy foods, making the summer EBT program permanent, and expanding SNAP eligibility for formerly incarcerated individuals. The American Families Plan also proposes a national paid family and medical leave program and universal pre-kindergarten, both of which research has shown have benefits for children’s health outcomes.8,9 President Biden and congressional Democrats also recently released a reconciliation budget resolution that includes expanded child tax credits and investments in universal pre-k, child care, paid leave, and education. Other policy actions at the local level can also address children’s well-being. For example, schools and school districts can support students as they transition back to school by creating a safe in-person learning environment, providing staff and resources to support students having difficulty transitioning, ensuring staff and teachers have access to mental health resources, and developing a trauma-informed plan to respond to COVID-19 related trauma.
COVID-19 and the health care disruptions, mental health challenges, and economic hardships stemming from COVID-19 all have implications for children’s health and their transition back to school in the fall. While returning to in-person learning can support children’s development and well-being, uncertainty remains around what in-person learning will look like as cases rise due to the Delta variant and the transition to “the new normal” may be difficult for some children and their families. Recent policy developments attempt to address the ongoing effects of the pandemic on children, and schools, parents, and policymakers may face additional pressure to support children during this time.