Options to Make Medicare More Affordable For Beneficiaries Amid the COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond
To date, the federal government has taken several steps to address the health and economic consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic, including sending billions of dollars to hospitals and other providers, providing economic stimulus payments to a majority of Americans, and requiring public and private insurers to provide free coverage of coronavirus testing. But the pandemic has exposed long-standing gaps in the U.S. health care system and brought fresh reminders of the health care affordability challenges facing many people, with and without insurance, including people with Medicare.
Medicare provides significant health and financial protections to more than 60 million Americans, but there are gaps in coverage and high cost-sharing requirements that can make health care difficult to afford, particularly for beneficiaries with modest incomes who lack supplemental coverage, such as employer-sponsored retiree health coverage, Medigap, or Medicaid. Beneficiaries are responsible for Medicare’s premiums, deductibles and other cost-sharing requirements, unless they have supplemental coverage or have incomes and assets low enough to qualify for the Medicare Savings Programs, which help cover Medicare Part A and Part B out-of-pocket costs, or the Medicare Part D low-income subsidy (LIS) program, which helps with Part D premiums and cost sharing only.
Beneficiaries in traditional Medicare with no supplemental coverage are vulnerable to high out-of-pocket expenses because Medicare, unlike marketplace and large employer plans, has no cap on out-of-pocket spending for covered services. But even those with supplemental coverage can face affordability challenges. Although Medicare Advantage plans are required to provide an annual out-of-pocket limit, beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans could still face high out-of-pocket costs, depending on the services they use, the drugs they take, and costs charged by their specific plan. And although beneficiaries with Medigap supplemental coverage have help with cost-sharing requirements for Medicare-covered services and protection against catastrophic expenses, premiums for these policies can be costly. With half of all Medicare beneficiaries living on an income of less than $30,000 per person, these affordability concerns could be compounded for some by the economic recession caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
This report analyzes several policy options that could help make health care more affordable for people covered by Medicare:
- Add an out-of-pocket limit to Medicare Part A and Part B.
- Add a hard cap on out-of-pocket drug spending under Medicare Part D.
- Expand Medicare premium and cost-sharing assistance to low-income Medicare beneficiaries through the Medicare Savings Programs.
- Expand Part D premium and cost-sharing assistance to low-income Medicare beneficiaries through the Part D Low-Income Subsidy Program.
For each of the options, we discuss implications and tradeoffs, including the added cost to the federal government of providing additional protection for beneficiaries. This report focuses on options to improve affordability of current Medicare benefits, rather than options that would expand the benefits Medicare covers, such as adding coverage of dental, vision, or hearing services. See Methodology for detail on data sources and methods.
Key Takeaways
The policy options examined in this analysis to help make health care more affordable for people covered by Medicare vary in the number of beneficiaries who could be helped and how much help they could receive (Figure 1). Each option would also have cost implications for Medicare and/or other payers, as described more fully in the longer discussion of each option following the introduction.
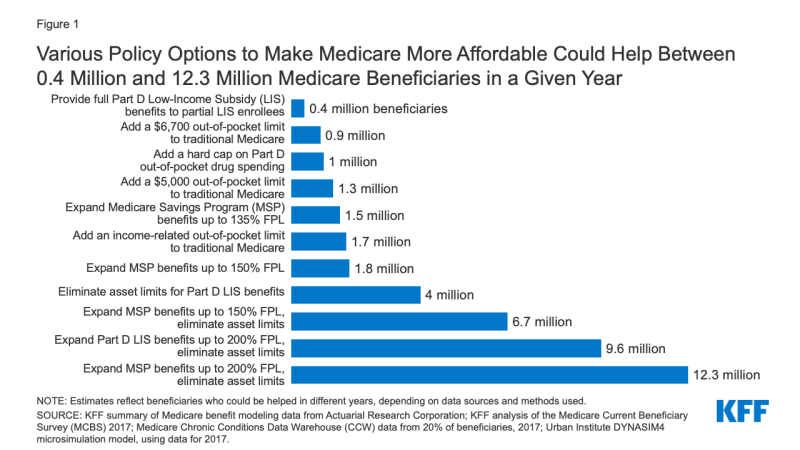
Figure 1: Various Policy Options to Make Medicare More Affordable Could Help Between 0.4 Million and 12.3 Million Medicare Beneficiaries in a Given Year
- Adding an annual out-of-pocket spending limit to traditional Medicare for Medicare Part A and B cost-sharing requirements would limit the risk of incurring high and potentially unaffordable expenses for nearly six million beneficiaries in traditional Medicare who have no supplemental coverage. The number of beneficiaries likely to be helped in any given year, and the average savings per beneficiary reaching the limit, would vary based on the amount of the out-of-pocket limit and what counts toward the limit. For example, adding a $6,700 out-of-pocket limit to Medicare Parts A and B would help 0.9 million beneficiaries in 2021, reducing their out-of-pocket costs for Medicare-covered services by approximately $2,700, on average, while adding an income-related limit would help 1.7 million beneficiaries, with average savings of nearly $2,200 in 2021. Adding an out-of-pocket limit would help people on Medicare with complex care needs, such as those who require one or more inpatient stays followed by a lengthy stay in a skilled nursing facility, or those who need high-cost medications that are covered under Medicare Part B. Adding an out-of-pocket limit to traditional Medicare would also lower Medigap premiums and premiums for employer or union-sponsored retiree health benefits for Medicare-eligible retirees, because the new out-of-pocket limit in traditional Medicare would reduce the amount of claims to be paid by these payers, while at the same time increasing Medicare Part B premiums, as Medicare assumes these costs above the limit.
- Adding a hard cap on out-of-pocket prescription drug spending to the Part D benefit would eliminate potential exposure to high drug costs for nearly 39 million beneficiaries currently enrolled in Part D plans who are not receiving low-income subsidies. Had the Part D benefit included a cap in 2017, with no other changes in benefit design, it would have lowered out-of-pocket drug spending for approximately 1 million Part D enrollees with high drug costs, with average savings of approximately $1,400 per enrollee that year.
- Expanding eligibility under the Medicare Savings Programs would help more low- and modest-income beneficiaries with Medicare premiums and cost-sharing requirements, with the number helped and the amount of assistance varying depending on the option. For example, expanding financial assistance under the Medicare Savings Programs by covering cost sharing for people currently receiving Part B premium assistance only would lower out-of-pocket costs for 1.5 million Medicare beneficiaries, with estimated average savings of $1,500 in 2020. Raising eligibility for the Medicare Savings Programs up to 150% or 200% of poverty and eliminating the asset test could help 7 million beneficiaries in total (expanding eligibility up to 150%) or 12.3 million beneficiaries (expanding eligibility up to 200%). Among these newly-eligible beneficiaries, estimated average savings would be $3,235 in 2020 for those who qualified for assistance with both premiums and cost sharing. For beneficiaries with incomes at 150% of poverty in 2020 ($19,140), this total savings represents 17% of their incomes. The group of beneficiaries who are helped under an approach that expanded eligibility up to 200% FPL with no asset test includes an estimated 3.9 million beneficiaries in communities of color, including 1.2 million Black beneficiaries, 1.9 million Hispanic beneficiaries, and 0.7 million beneficiaries in other racial and ethnic groups.
- Expanding eligibility under the Part D Low-Income Subsidy program would help more low and modest income beneficiaries with their Part D prescription drug plan premiums and cost-sharing requirements, with the number helped and the amount of assistance varying depending on the option. For example, providing full Part D low-income subsidies to beneficiaries who would otherwise be eligible for partial subsidies would lower prescription drug-related costs for 0.4 million Medicare beneficiaries, with estimated saving ranging from $270 to $560 in 2020, depending on the level of help they are eligible for under current law. Raising eligibility for Part D premium and cost-sharing subsidies from 150% FPL to 200% FPL, and eliminating the asset test would lower prescription drug-related costs for 9.6 million Medicare beneficiaries. Part D enrollees who are not currently eligible for premium or cost-sharing assistance would see estimated savings of $850 in 2020 on their Part D prescription drug cost sharing and premiums, on average, if they qualified for full LIS benefits.
As noted above, each of these options would also have cost implications for Medicare that would vary depending upon specific policy features. In addition, some of these options would have spillover effects for other payers (Medicaid, employers and unions). These effects are discussed more fully below.
