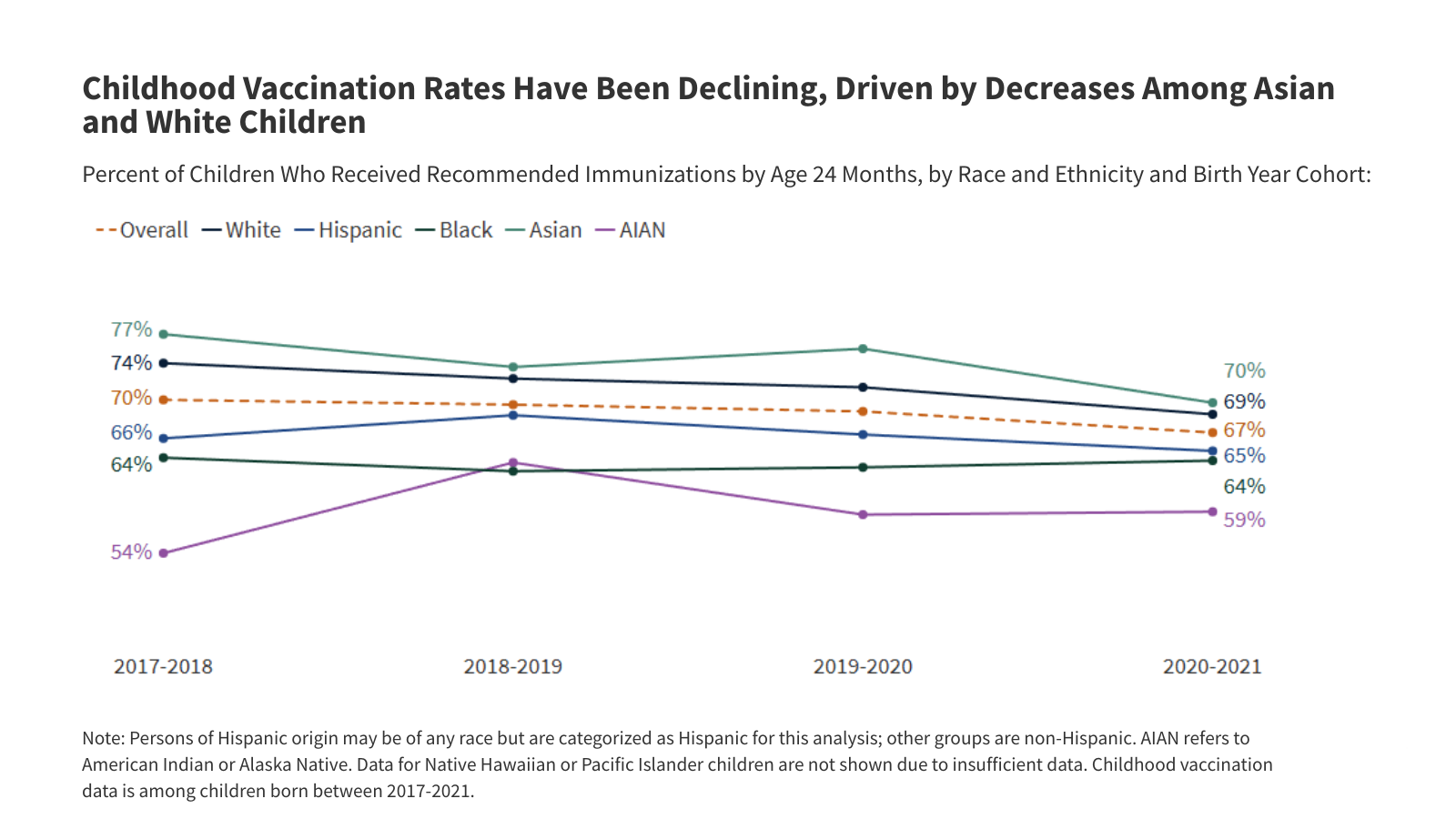
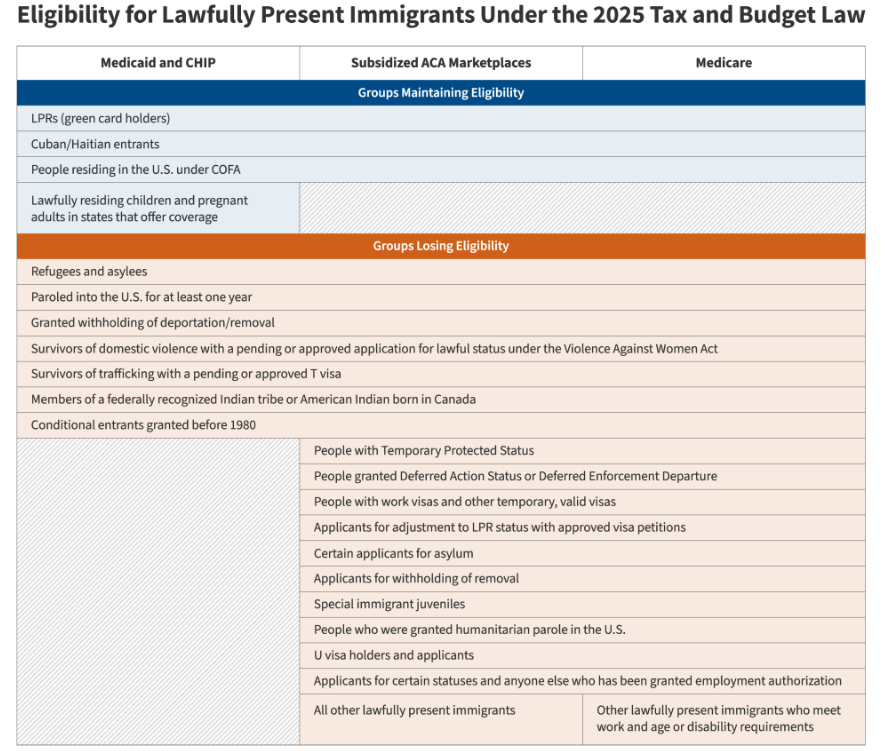
KFF-New York Times Survey: Immigrants Report Rising Fear, Negative Economic and Health Impacts, and Changing Political Views During the First Year of President Trump’s Second Term
The 2025 Survey of Immigrants, a partnership between KFF and The New York Times, takes an in-depth look at the experiences of immigrants during the first year of President Trump’s second term, including their worries related to increased immigration enforcement, their health and economic wellbeing, and the political views and preferences of immigrant voters. The survey paints a portrait of families under strain — where fear of detention and economic instability are negatively impacting immigrants’ health and reshaping immigrant families’ daily lives and views of U.S. political parties.
Read the News Release | Explore The New York Times’ Reporting