Medicaid
new and noteworthy
Medicaid: What to Watch in 2026
In this brief, KFF explores how state fiscal pressures are likely to converge with the implementation of the 2025 reconciliation law to affect Medicaid coverage, financing, and access to care over the next year, especially leading up to the midterm elections.
Medicaid and work
Challenges with Implementing Work Requirements: Findings from a Survey of State Medicaid Programs
To better understand how states are preparing for Medicaid work requirements, states were asked to discuss anticipated challenges to implementing work requirements by the end of 2026, including related system changes and data matching.
understanding medicaid
Medicaid Financing
Medicaid represents $1 out of every $5 spent on health care in the U.S. and is the major source of financing for states to provide health coverage and long-term care. This brief examines key questions about Medicaid financing and how it works.
Medicaid and Provider Taxes
All states except Alaska cover some state Medicaid costs with taxes on health care providers. This brief uses data from KFF’s 2024-2025 survey of Medicaid directors to describe current practices and the federal rules governing them.
5 Facts: Medicaid and Hospitals
Absorbing reductions in Medicaid spending could be challenging for hospitals, particularly for those that are financially vulnerable. This brief provides data on the reach of Medicaid across hospitals, patients, and charity care.
Medicaid Home Care in 2025
This issue brief provides an overview of what Medicaid home care (also known as “home- and community-based services”) is, who is covered, and what services were available in 2025.
5 Facts: Medicaid Program Integrity
This brief explains what is known about improper payments and fraud and abuse in Medicaid and describes ongoing state and federal actions to address program integrity.
2025 Medicaid Home Care survey
Eligibility, Enrollment, and Renewal Policies
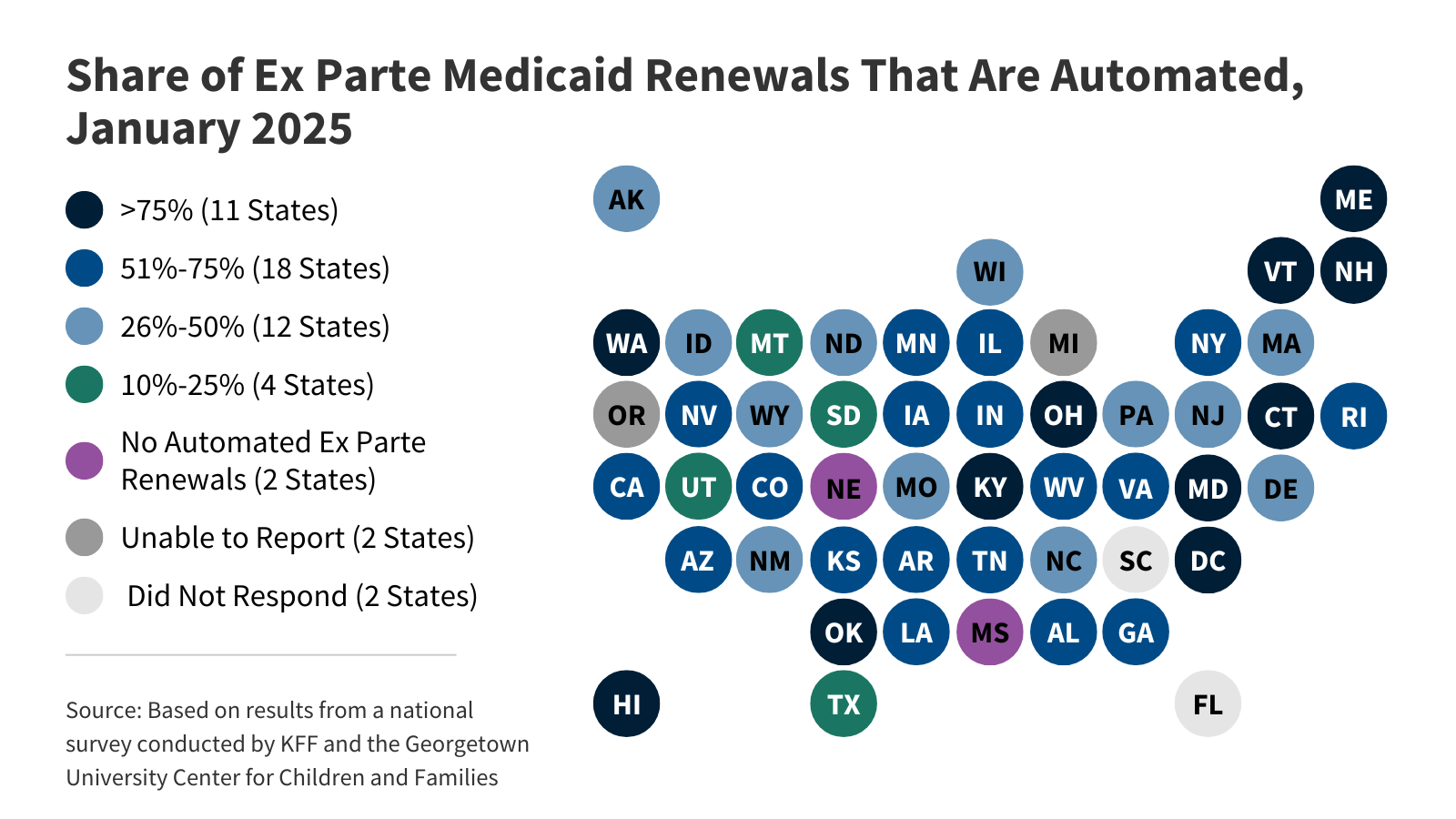 KFF's survey findings capture state actions that seek to improve the accuracy and efficiency of Medicaid and CHIP enrollment and renewal processes, as of January 2025.
KFF's survey findings capture state actions that seek to improve the accuracy and efficiency of Medicaid and CHIP enrollment and renewal processes, as of January 2025.Seniors and People with Disabilities
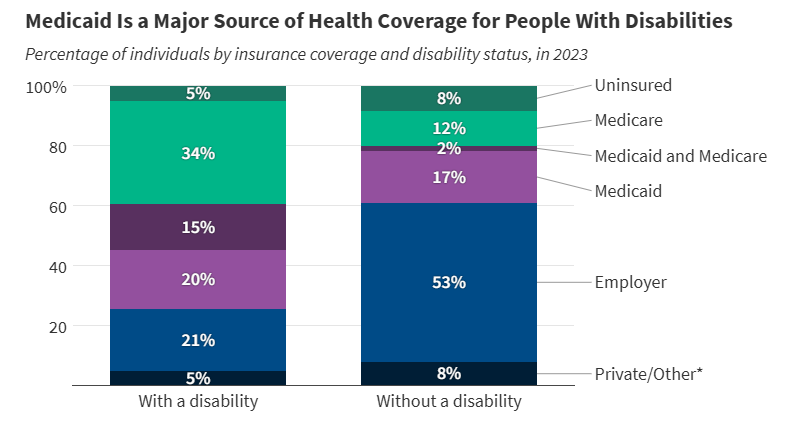 More than 1 in 3 people with disabilities (15 million) have Medicaid (35%). In comparison, only 19% of people without disabilities have Medicaid.
More than 1 in 3 people with disabilities (15 million) have Medicaid (35%). In comparison, only 19% of people without disabilities have Medicaid.Children with Special Needs
 Amid debates about proposed cuts to federal Medicaid spending, this brief analyzes key characteristics of children with special health care needs and explores how Medicaid provides them with coverage.
Amid debates about proposed cuts to federal Medicaid spending, this brief analyzes key characteristics of children with special health care needs and explores how Medicaid provides them with coverage.People With Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities
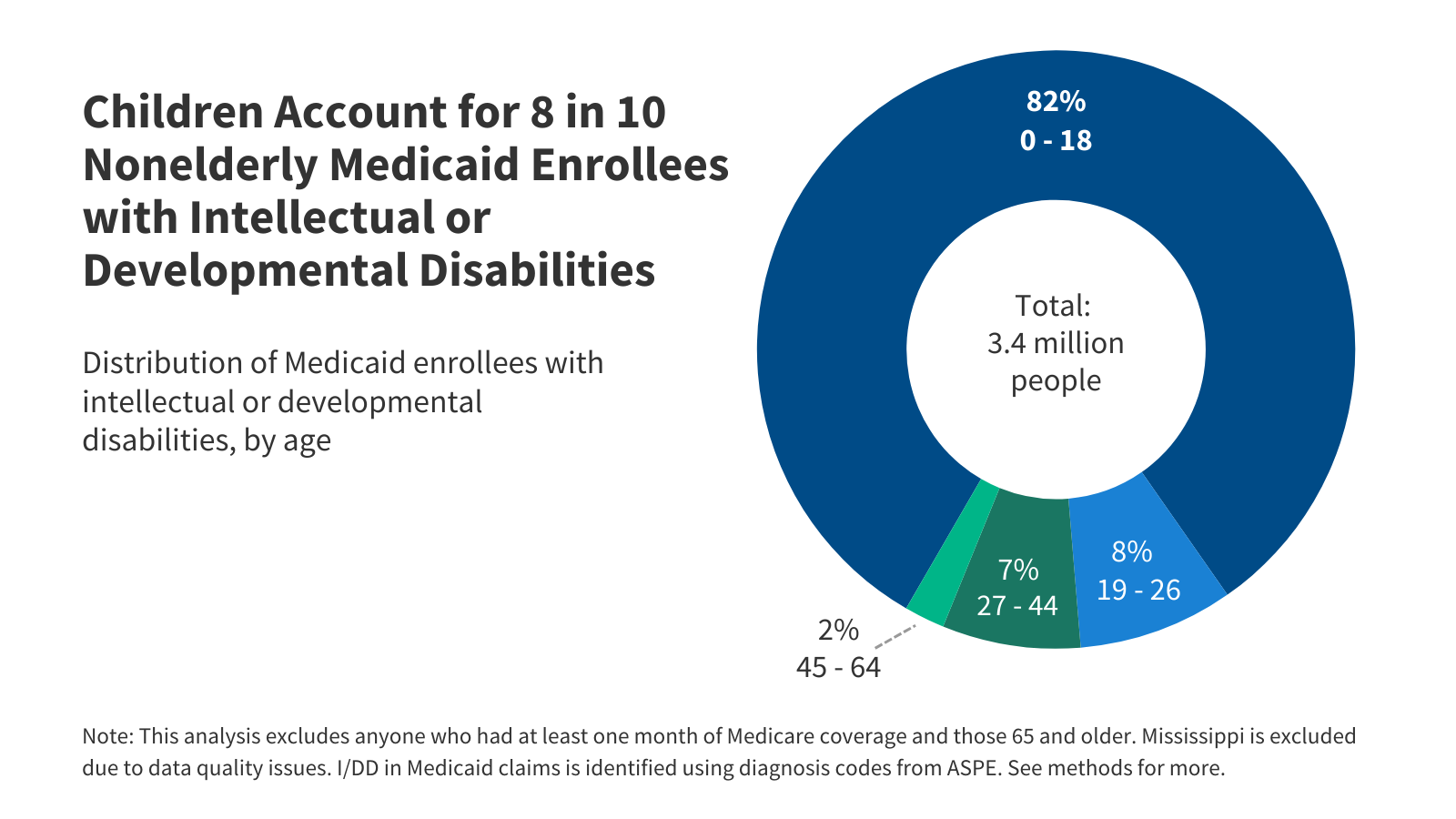 Among the estimated 8 million people with intellectual and developmental disabilities (I/DD), over three million have Medicaid coverage.
Among the estimated 8 million people with intellectual and developmental disabilities (I/DD), over three million have Medicaid coverage.Adults with Chronic Conditions
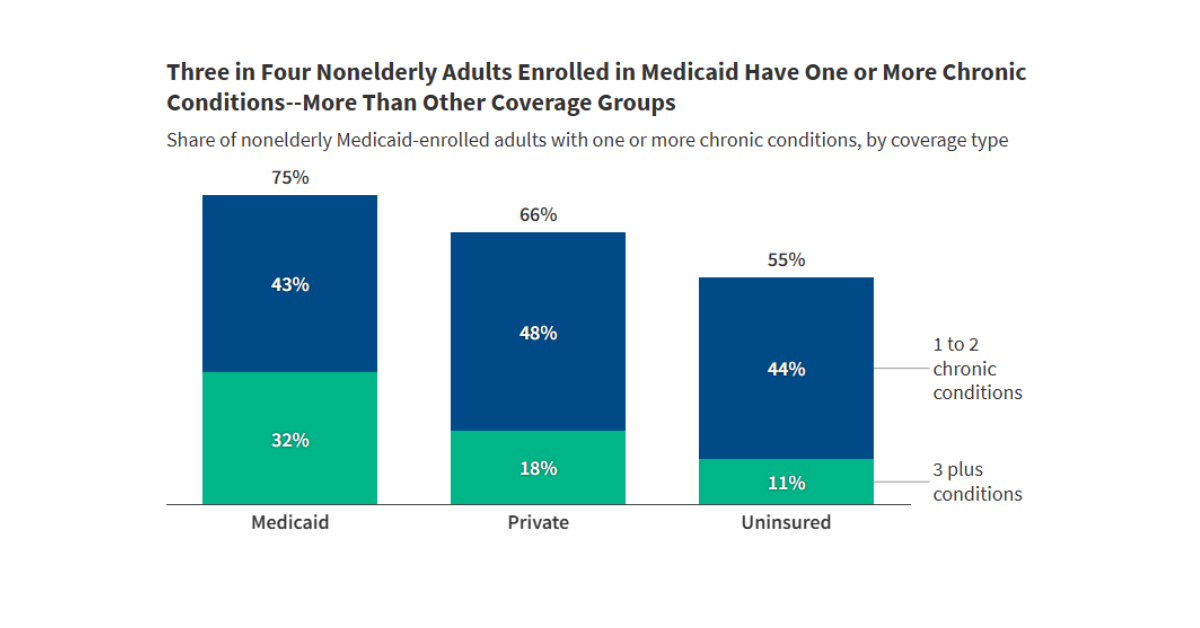 Among working age adults enrolled in Medicaid, approximately three quarters have one or more chronic conditions, and nearly one-third have three or more.
Among working age adults enrolled in Medicaid, approximately three quarters have one or more chronic conditions, and nearly one-third have three or more.
Latest News
-

What the Health? From KFF Health News: RFK Jr.’s Very Bad Week
-

Florida no amplió Medicaid, pero igual algunos legisladores quieren imponer requisitos de trabajo
-

Florida Hasn’t Expanded Medicaid. Lawmakers Want To Add Work Requirements Anyway.
-

Journalists Explain a Spat Over Sugary Coffee and How Measles Fools Doctors
Subscribe to KFF Emails
Choose which emails are best for you.
Sign up here
