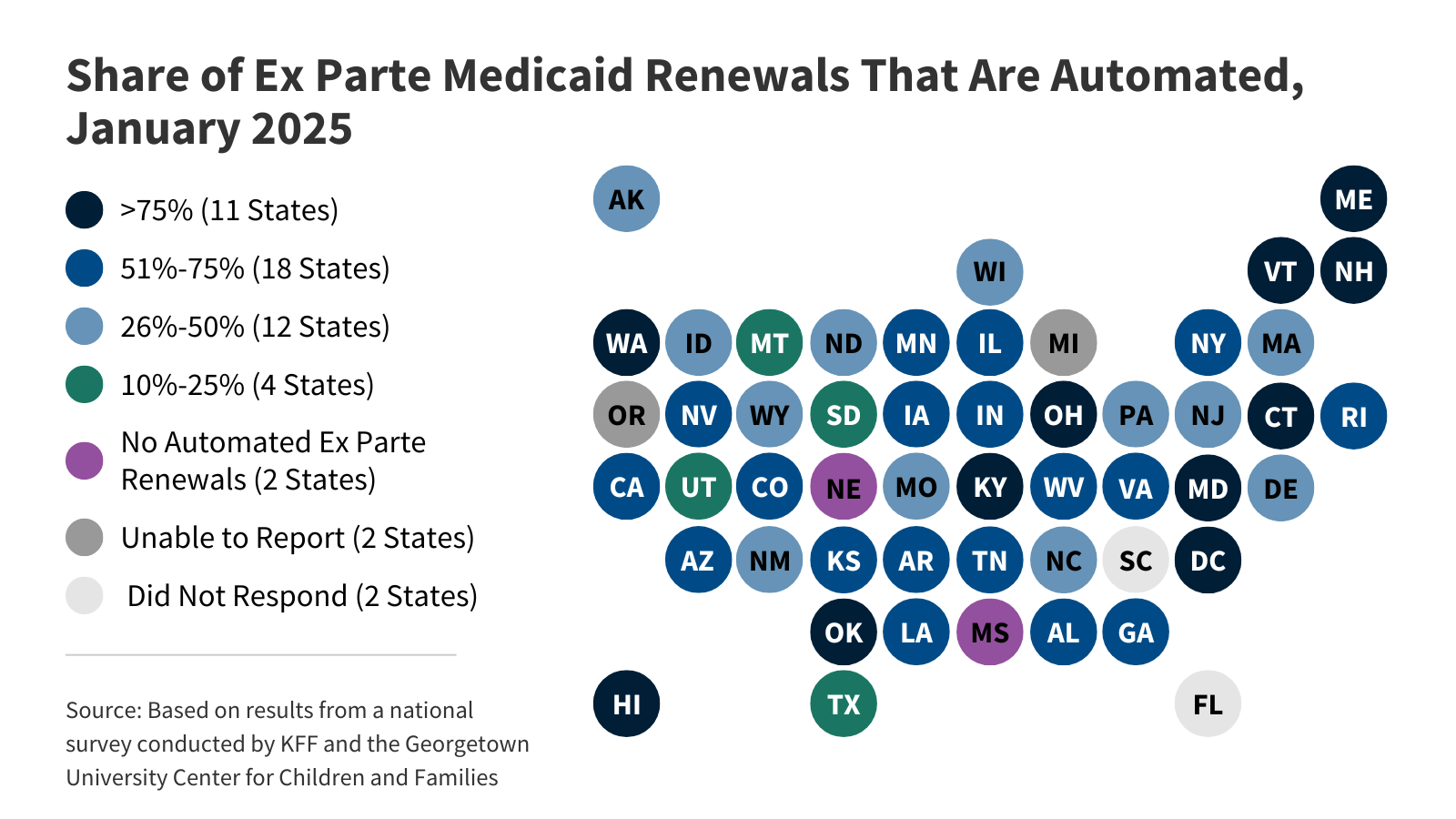
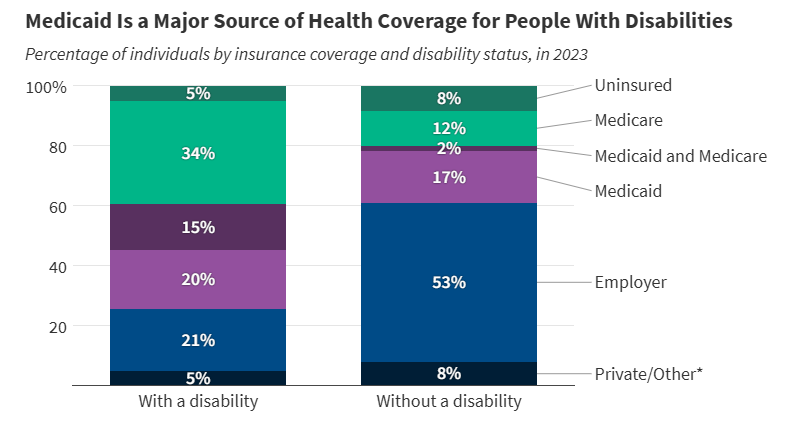
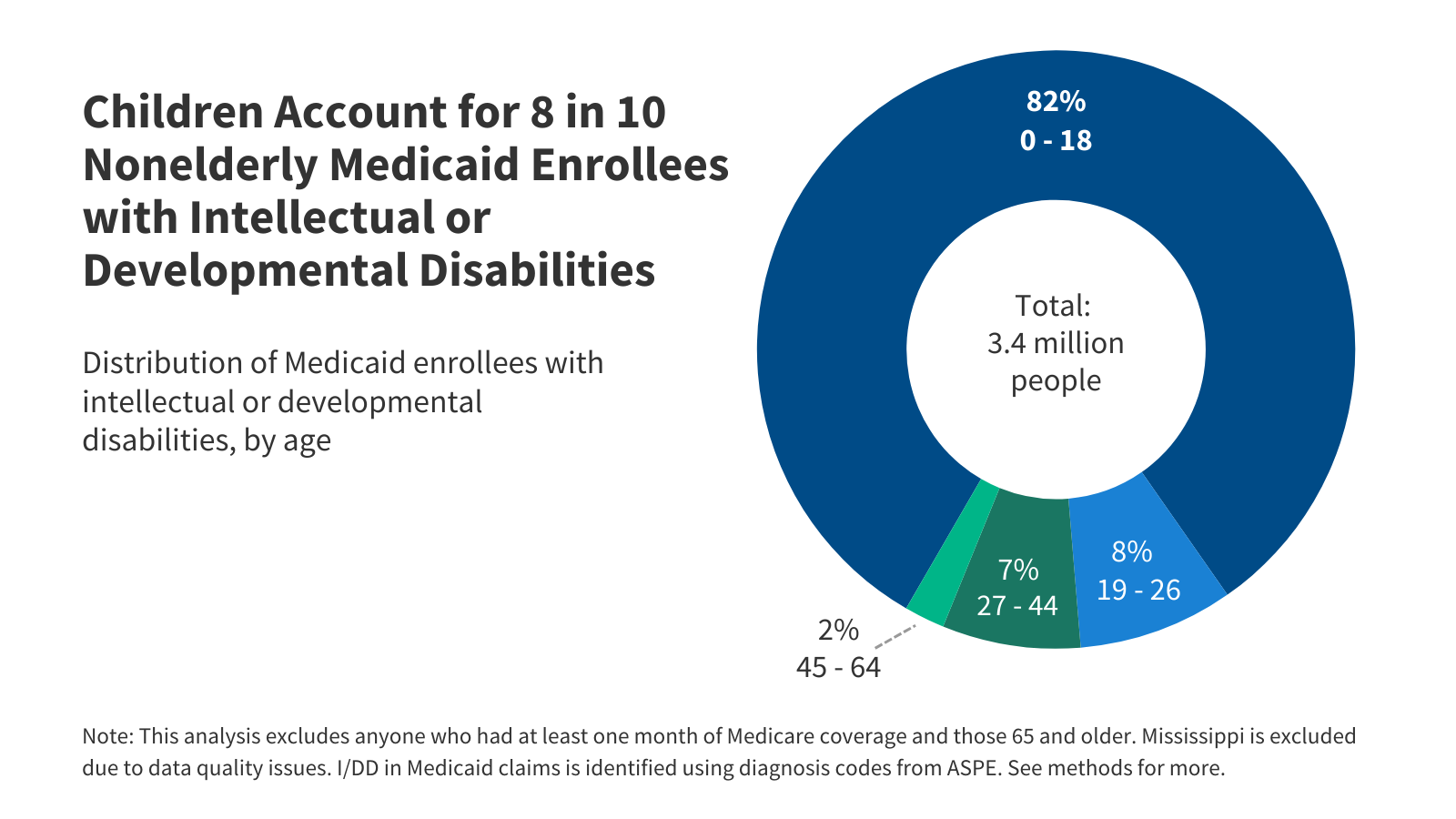
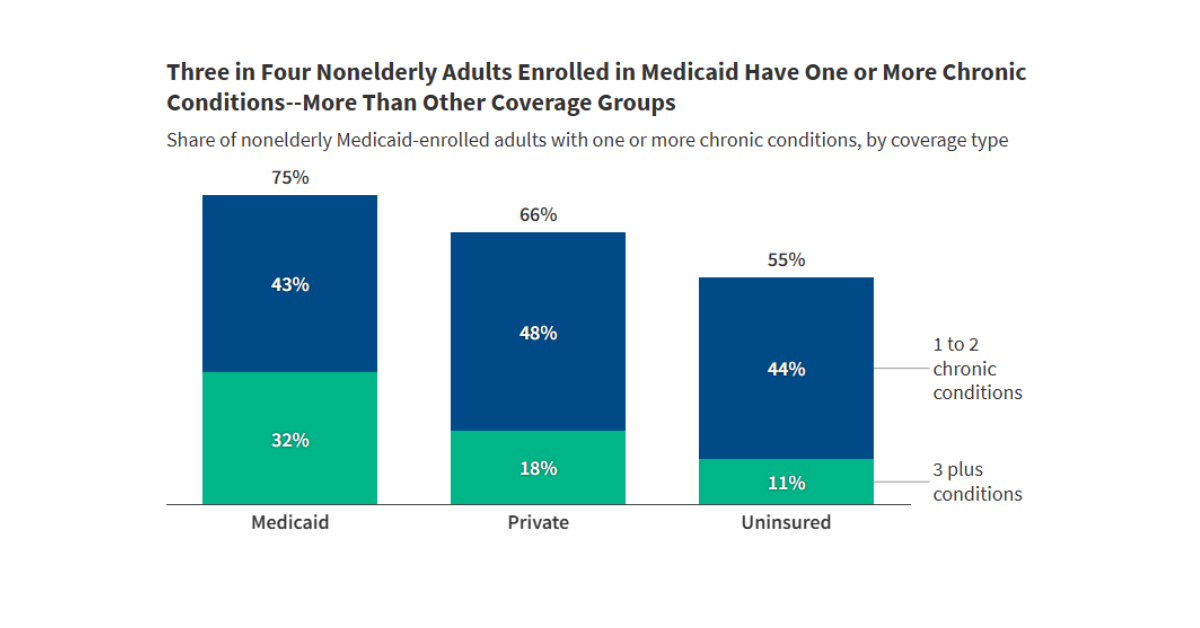
A View of Medicaid Today and a Look Ahead: Balancing Access, Budgets and Upcoming Changes
KFF's 25th annual Medicaid budget survey report highlights certain policies in place in state Medicaid programs in state fiscal year (FY) 2025 and policy changes implemented or planned for FY 2026.