Mental Health Parity at a Crossroads
Issue Brief
More than 25 years after the first federal mental health parity protections were put in place, adequate coverage for behavioral health (BH) care – including both mental health and substance use conditions –remains elusive for many consumers with health insurance.1 Federal BH parity rules require health plans that offer BH coverage to ensure that financial requirements (such as deductibles, copayments, coinsurance, and out-of-pocket limits) and treatment limits (such as day and visit limits as well as nonquantitative limits on benefits such as prior authorization) on these benefits are no more restrictive than those on medical and surgical benefits. The COVID-19 pandemic has heightened awareness and exacerbated existing challenges in BH. Strengthening BH parity protections is just one part of a larger policy discussion that includes addressing the BH workforce shortage, rising BH treatment needs among children and youth, an inadequate health care infrastructure to address those in crisis, and the need for improved coordination and integration of primary care and BH care in the health care delivery system.
All of these issues contribute to the access and coverage challenges in health insurance that BH parity was supposed to address. The stakes are high for coverage protection, as nearly 90% of nonelderly individuals with a BH condition have some form of health coverage. Despite having coverage, many insured adults (36%) with moderate to severe symptoms of anxiety and depression did not receive care in 2019. There have been consistent calls for more federal guidance on the specific protections in the federal BH parity law, as well as for increased enforcement. As Congress2 debates reforms to address these concerns in BH care, and as federal agencies plan to update parity regulations, this brief explains the federal BH parity requirements – including who they apply to and how they’re enforced — and sets out key policy issues.
Federal BH Parity Protections
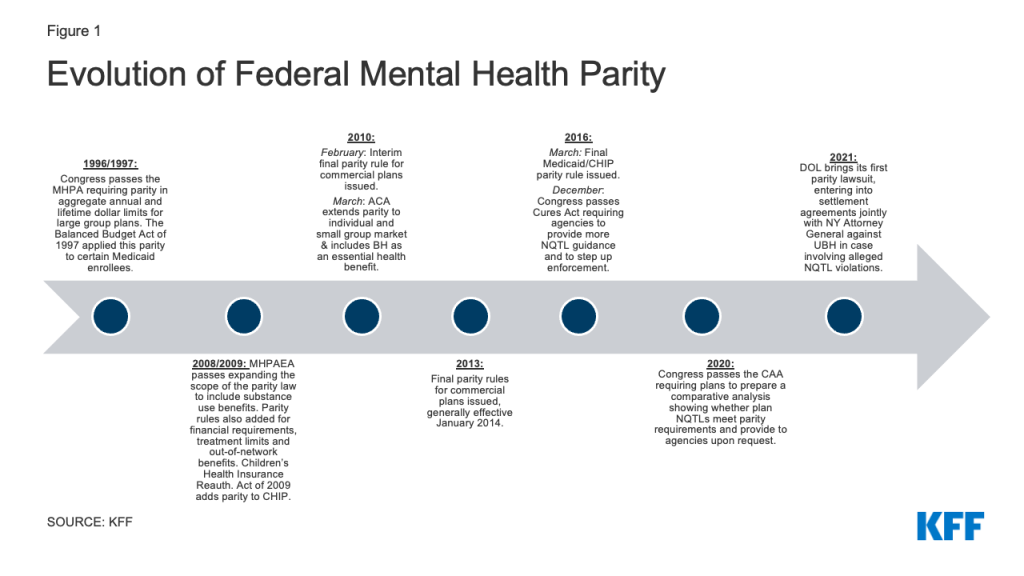
Federal protections for BH coverage sought to correct historical differences in how health insurance covered this care when compared to medical/surgical benefits. The focal point of these protections has evolved over the years from the narrow initial federal law, the Mental Health Parity Act of 1996 (MHPA), to the broader protections in the current law, the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act of 2008 (MHPAEA) (Appendix Figure 1).
With MHPAEA, an initial focus on ensuring that consumers were not subject to higher cost sharing and more restrictive day and visit limits for BH shifted to looking at disparities in treatments limits in coverage that are not expressed numerically. These so-called “nonquantitative treatment limits” or NQTLs include plan features that limit the scope or duration of care such as prior authorization requirements and medical necessity reviews, standards for provider admission to a network, and provider reimbursement rates.
Federal regulations implementing parity for commercial plans and for Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) have set out substantially similar protections (See Appendix Table 1 for major differences between commercial parity and Medicaid). These are detailed and complex standards making it a challenge for consumers with coverage to know what practices violate the law. Federal agencies have issued FAQs and other guidance for both commercial and Medicaid/CHIP to explain how these standards work. The basic protections are described below.
who does the law apply to?
Federal BH parity rules apply to most health coverage, public and private, but do not apply to Medicare. Table 1 summarizes the basic rules and exceptions. Parity applies to all health coverage in the individual, small and large group insurance markets, as well as to all private employer-sponsored plans (insured and self-insured) with the exception of self-insured employer plans covering groups of no more than 50 employees, “retiree only” plans, short-term limited duration coverage and coverage considered “excepted benefits.”3 It also applies to self-insured state and local governmental plans (called nonfederal governmental plans), though these plans have the ability to opt out of MHPAEA protections, as hundreds of plans across 31 states currently do.4
| Table 1: When Do Federal BH Rules Apply? | ||
| Plan Type | Apply? | Exceptions |
| Private Employer-sponsored Group Health Plan: | ||
| Self-Insured | Yes | Does not apply to self-insured small employer plans, retiree only plans and excepted benefit plans |
| Insured | Yes | Does not apply to retiree only plans and excepted benefit plans |
| State & Local Government Employer-sponsored Group Health Plan (“Non-federal governmental” plans): | ||
| Self-insured | Yes | Can annually opt out of MHPAEA compliance |
| Insured | Yes | |
| Individual insurance plan (on or off exchange) | Yes | Does not apply to excepted benefit plans |
| Small group insurance plan (on or off exchange) | Yes | Does not apply to retiree only and excepted benefit plans |
| Medicaid: | ||
| MCO/PHIP/PAHP* (providing Medicaid-covered services to managed care enrollees) | Yes | |
| Alternative Benefit Plan (both fee-for-service & managed care) | Yes | ABPs services provided fee-for-service do not have to comply with MHPAEA rules regarding aggregate lifetime and annual dollar limits. |
| Fee-for-Service (FFS) | No | Applies to state plan services provided on a FFS basis to MCO enrollees (carve-outs from MCO contract); Most parity provisions apply to ABP services provided FFS |
| Children’s Health Insurance Plan (CHIP) | Yes | Parity does not apply to CHIP Medicaid expansion programs that provides services on a FFS basis only, with no MCO enrollees. |
| Medicare Fee-for-Service | No | |
| Medicare Advantage | No | |
| NOTES: * MCO (Medicaid managed care organization), PHIP (Prepaid inpatient health plan) and PAHP (Prepaid ambulatory health plan) are types of delivery system that provide Medicaid benefits. | ||
Substantially similar parity rules apply to enrollees in certain Medicaid coverage. Medicaid regulations apply parity to any Medicaid service provided to Medicaid managed care (MCO) enrollees, regardless of whether those services are provided by the MCO or on a fee-for-service (FFS) basis. Parity also applies to Medicaid alternative benefit plans (ABP) – which cover adults under the Affordable Care Act’s Medicaid expansion — whether delivered through managed care or FFS.5
Parity also generally applies to coverage under CHIP regardless of the delivery system.6
MHPAEA does not apply to Medicare, either fee-for-service or Medicare Advantage.7 Although MHPAEA does not apply to Medicare, the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act of 2008 did lower cost sharing for outpatient mental health services to match cost sharing for Medicare outpatient medical treatment.
The MHPAEA law does include a cost exemption provision that would allow plans to apply for a temporary exemption from compliance if costs exceed a certain threshold in a given plan year.8 Medicaid parity regulations did not extend this cost exemption in the statute to Medicaid and CHIP.
are plans required to cover bH services under MHPAEA?
MHPAEA does not itself require plans to provide BH benefits, nor does it require coverage of any particular treatment or condition. Other laws requiring coverage of certain BH services apply to some plans and not others, creating a complicated landscape to navigate for consumers seeking these services. The landscape is best summarized as follows:
BH services are among “essential health benefits” that the ACA requires plans to cover in the individual and small group insurance market. The ACA required these plans to cover items and services for “mental health and substance use disorder services, including behavioral health” equal in scope to a “typical employer plan.” Covered EHB behavioral health benefits are not uniform from state to state, since EHB regulations require each state to pick a set of covered benefits from one of four “EHB benchmark plans.”9 The ACA’s essential health benefits requirement does not apply to large employer plans.
Most states have some form of BH coverage mandate that will apply to fully-insured employer plans and individual market policies. These requirements differ from state to state, and could require insurers to cover specific services such as applied behavioral analysis (ABA) for autism. These requirements might also set process rules that insurers must follow such as limits on use of prior authorization for a BH item or service.
Federal Medicaid law does not require states to cover any particular BH benefit. While Medicaid plays a major role as a source for BH coverage, covering a large percentage of adults in the U.S. with BH conditions, states have the flexibility to determine which services to offer in their Medicaid programs, subject to federal minimum requirements. Some BH services may be covered in mandatory state plan categories such as physician services or outpatient hospital services, while others are covered under optional state plan categories. As discussed earlier, instead of a state plan benefit package, states must provide ABP benefits to newly eligible adults if they choose the ACA’s Medicaid expansion. ABPs, similar to the ACA essential health benefit framework, are required to cover BH equivalent to a state’s chosen private sector benchmark. Note that Medicaid does not pay for certain inpatient BH services due to the Medicaid program’s “institutions for medical disease” (IMD) exclusion.10 CMS stated in Medicaid parity regulations that it considers this exclusion beyond the scope of the parity regulation.
Self-insured private employer plans – which are typically offered by larger employers but increasingly by smaller employers as well — have no requirement to cover any BH services, as neither state mandates nor the ACA’s essential health benefit requirements apply to these plans. Parity protections for these plans are only triggered if these employers offer BH coverage. While most employers provide some form of BH coverage, there is a growing amount of private litigation about whether the parity law requires that plans cover specific BH treatments that are either excluded or determined not medically necessary under the plan.
WHAT IS CONSIDERED A BH BENEFIT VERSUS A MEDICAL BENEFIT?
While the parity rules require plans to compare coverage for BH to medical/surgical coverage in each classification, there is no standard definition for what is a BH condition versus what is a medical condition.
The parity regulations provide that plans and states must use a “generally recognized” standard for defining what benefits are considered BH items and service but does not require use of a specific standard. A standard is considered generally recognized when it is generally accepted in the relevant medical community.11 Examples of generally accepted standards mentioned in MHPAEA regulations include the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), the International Classification of Disease (ICD) or state guidelines. of the DSM as the baseline, for instance, would include a broad range of conditions as BH, such as sleep apnea or Alzheimer’s disease, according to the CMS Parity toolkit.12 Use of other standards might narrow what is considered BH. As a result, what diagnoses are treated as BH versus medical could differ from plan to plan. This may come up for certain conditions such as autism or nicotine addiction resulting in uneven protections.
The 21st Century Cures Act of 2016 (the Cures Act) did attempt to clarify that for the purposes of MHPAEA, treatment of eating disorders is considered a BH treatment, not medical. This requires treatments such a nutritional counseling for anorexia to be considered BH treatment under the parity law.
what are the parity standards?
Federal parity regulations include protections in three distinct areas—quantitative standards, nonquantitative treatment limits and disclosure rules– each with its own set of rules. For quantitative and nonquantitative rules, commercial plans and state Medicaid agencies must evaluate whether there is parity between medical and BH benefits separately within specific benefits classifications. BH benefits for inpatient in-network care, for example, is compared to medical care benefits covered in the same inpatient in-network classification. Commercials plans must perform an analysis comparing medical to BH benefits in each of six classifications:
- Inpatient, in-network benefits
- Inpatient, out-of-network benefits
- Outpatient, in-network benefits
- Outpatient, out-of-network benefits
- Prescription drug benefits
- Emergency benefits
For Medicaid and CHIP, states and plans providing this coverage must compare benefits within four of the six classifications, the two out-of-network classifications are not included.
The three main requirements of the federal BH parity regulations are discussed below:
1. Quantitative Standards
MHPAEA affects how plans and state Medicaid agencies can design their patient cost-sharing and quantitative restrictions on BH benefits. The rules fall into one of three categories:
Financial requirements and quantitative treatment limits. Plans cannot place financial requirements (copays, coinsurance) and quantitative limits (day and visit limits) on BH that are more restrictive than the predominant financial requirement or quantitative limit applied to substantially all medical benefits. The federal agencies defined these terms and developed a formula to evaluate each financial requirement and quantitative limitation. The tests are the same for private coverage and Medicaid, (although longstanding Medicaid rules already limit cost sharing, with some populations and services exempt from any cost sharing).13 These are complicated tests that typically involve looking at medical and surgical claims data to estimate the total dollars expected to be paid for medical/surgical benefits in a given year for each financial requirement and treatment limitation.
“Cumulative” financial requirements and treatment limits. The parity law prevents the application of a separate cumulative financial requirement (deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums) or cumulative quantitative treatment limit (such as caps on visits) to just BH benefits. This means that both BH and medical/surgical benefits must count toward the same deductible, out-of-pocket maximum, and visit cap. The Medicaid parity rules diverge slightly by not prohibiting cumulative quantitative treatment limits such as visit caps from accumulating separately for BH and medical/surgical care.14
Aggregate dollar limits. A different quantitative test15 applies to annual and lifetime dollar limits, but the ACA’s prohibition on aggregate dollar limits on EHBs now largely restricts these types of limits for most commercial plans.
2. Non-Quantitative Treatment Limits
Any limitation on coverage other than numerical limits is considered an NQTL. This could bring in an endless variety of coverage design standards. MHPAEA regulations provide a non-exhaustive list of common NQTLs, such as medical management standards that limit benefits based on medical necessity or whether treatment is experimental or investigational. This would include any prior authorization requirement to obtain a BH benefit. Other NQTLs include formulary design for prescription drugs, network tier design, standards for provider admission to participate in a network (including reimbursement rates), restrictions in coverage based on geographic location, facility or provider type, standards for providing access to out-of-network providers.16 The Department of Labor (DOL) has issued several sets of FAQ guidance discussing specific types of NQTLs.
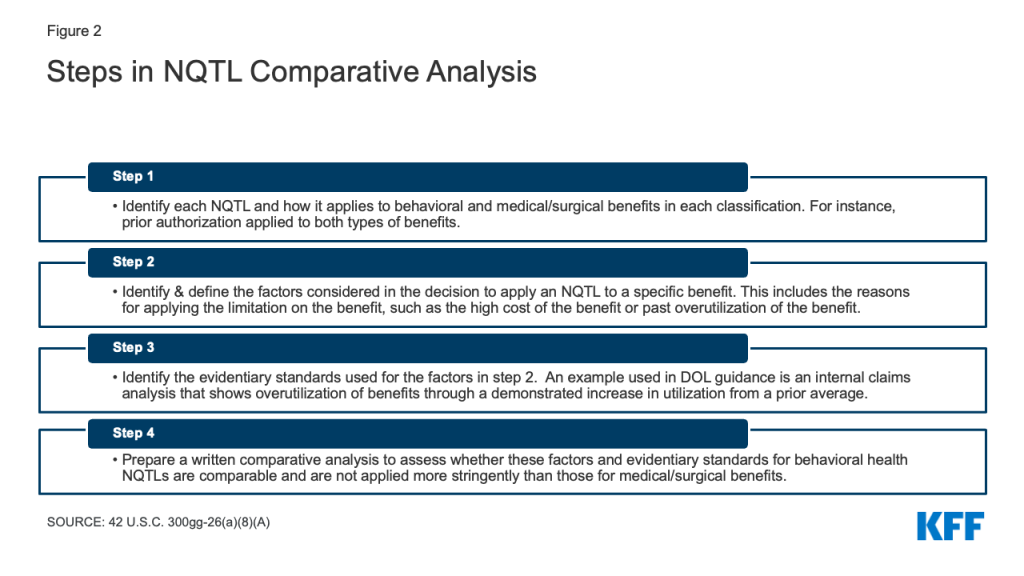
Under parity regulations, plans cannot apply a NQTL to a BH benefit unless the “processes, strategies, evidentiary standards and other factors” used to apply that restriction are “comparable to and applied no more stringently” to these benefits than they are to medical surgical benefits. This standard is challenging to implement as there are no bright line rules for determining what is “comparable” and “more stringent,” when comparing benefits. A multistep process (Appendix Figure 2), added to the MHPAEA statute as part of the 2020 Consolidated Appropriations Act, is used to compare BH NQTLs to those for medical/surgical benefits. This requires that plans evaluate the rationale for applying these restrictions to BH benefits and the evidence that backs up the rationale.
Outcomes as a red flag for possible parity violation. Federal agency NQTL guidance has consistently said that outcomes are not determinative of parity compliance. For instance, higher rates of claims denial for preauthorized BH care when compared to medical preauthorization claims, is not alone a violation of the parity law. However, the DOL has said that disparities in this type of data may be a warning sign of a possible problem that the processes used are not comparable. The DOL self-compliance tool suggests that plans evaluate average denial rates of BH and other medical/surgical claims. There is no requirement, however, as part of the NQTL comparative analysis to evaluate this or other data. At least one health care advocacy organization has developed for employers a model data request form that employers and their third-party vendors can use to evaluate compliance for certain NQTLs. Also, New York is one example of a state that has used data analysis as part of their parity evaluation of commercial insurers.
Internal Clinical Guidelines as NQTL. Agency guidance has included the use of medical necessity criteria as a common example of an NQTL. For instance, in an example included in a recent enforcement report to Congress, CMS required an issuer to remove continued stay criteria for a BH condition that required a demonstration of significant improvement in an enrollee’s condition to warrant continued coverage. There were no similar criteria applied to medical/surgical criteria in the same classification.17
“Home grown” medical necessity standards examined. Much more complicated issues arise when plans make coverage decisions using medical management criteria based on internal clinical guidelines developed by a health plan. An open question under MHPAEA and other laws is whether the use of internal clinical guidelines unique to a specific plan violates parity by applying to BH claims medical necessity standards that are not comparable and are more stringent than those used for medical necessity decisions on medical claims. These guidelines have been criticized as narrowing the scope of covered BH treatments and as inconsistent with generally accepted standards of practice. Wit v. United Behavioral Health (UBH), a class action lawsuit challenging the use of these internal clinical criteria as medical necessity criteria, has received national attention. Box 1. Some states have insurance coverage rules that require the use of specific guidelines or include additional oversight of the clinical guidelines used by private insurers. Rhode Island and Illinois, for example, require use of criteria developed by the American Society of Addiction Medicine when reviewing relevant claims for substance use treatment. California requires plans in state’s private insurance market to cover medically necessary treatment for BH under the same terms and conditions as done for medical care. Insurers are prohibited from using their own clinical coverage criteria and must choose generally accepted guidelines developed by an independent nonprofit organization, subject to state approval.
Box 1: Summary of Wit. v. United Behavioral Health (UBH)
This ongoing class action litigation, while not a case brought under MHPAEA, challenges the use of internal clinical guidelines for BH in making coverage decisions. The named plaintiffs in the case were largely covered by employer-sponsored coverage insured or administered by UBH. Seeking treatment for their substance use conditions, they sued after their plan denied claims for residential or intensive outpatient treatment. In 2019, a California federal district court held that UBH applied overly restrictive internal clinical guidelines to deny coverage of thousands of BH claims violating certain provisions of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA)—the federal law that regulates private sector employer-sponsored health plans. The court concluded that the guidelines were not consistent with generally accepted standards of care because they improperly focused on addressing acute symptoms and stabilizing crises rather than providing effective treatment for the plaintiffs’ underlying BH conditions. The court also concluded that UBHs’ use of these guidelines benefited UBH’s financial bottom line in violation of ERISA. UBH was ordered to reprocess over 60,000 claims, drop its internal guidelines, and choose generally accepted guidelines develop by an independent nonprofit organization.
The Ninth Circuit federal court of appeals overturned this decision in March 2022, stating that the lower federal court should have deferred to the decision of UBH in denying benefits, because their decision was “not unreasonable.” UBH, according to the court, was not required to cover the care involved even though the treatment may have been consistent with generally accepted standards of care. Plaintiffs have appealed the decision to the full panel of judges on the Ninth Circuit.
NQTLs that affect Network Adequacy. With many reports of narrow network for BH services, there is some potential to address these problems under the parity law. The parity regulations include several plan limitations related to network adequacy as NQTLs that plans must evaluate under the parity framework. This includes rules for provider admission to a network, including reimbursement rates, and restrictions on facility types covered in-network. As with other NQTLs, the inquiry is simply whether the process for setting out standards in these areas is comparable and not more stringent for BH providers versus medical providers. Disparate numbers of BH and medical/surgical providers in a plan’s network might be an indicator of a parity violation but is not itself a violation. Examples of violations in FAQ guidance include:
Setting a network adequacy standard only for medical providers. Setting an appointment wait time standard for admission of medical providers to a network but having no equivalent network adequacy standard for BH providers violates the parity rules, according to agency FAQs18 .
Using different methodologies for setting reimbursement rates for in network providers. Agency guidance has also stated that a methodology that reimburses in-network BH providers at the Medicare rate, while reimbursing medical health providers at two times the Medicare reimbursement violates the parity law. The agencies have also called out as not permissible under MHPAEA disparities in the method used to determine reimbursement for nonphysican practitioners who provide medical care versus nonphysican practitioners who provide BH care.19
Blanket exclusions as NQTL. An exclusion of all benefits for a particular BH condition is not considered a treatment limit under MHPAEA regulations.20 While other state or federal laws require coverage of certain BH items or services, these types of exclusion do not explicitly violate parity.21 However, if a plan covers treatment for a specific BH condition, the plan must cover treatment for that condition in every classification in which medical benefits are covered. The reach of this provision is unclear, but the rule often comes up in practice to prohibit commercial plans from excluding all substance use disorder benefits in the inpatient, out-of-network classification, if benefits for that substance use disorder are covered in all of the other five classifications. This type of exclusion is considered an NQTL that violates parity.
Private litigation under commercial parity rules has often involved challenges to exclusions of specific treatments such as ABA for autism. The cases are based on language in the MHPAEA law that, plans must ensure that. “…no separate cost sharing requirements or separate treatment limitations apply only to mental health and substance use disorder benefits.” For example, a recent appellate decision in the First Circuit Court of Appeals, N.R. v. Raytheon, allowed a parity act challenge to an exclusion for habilitative services to move forward. That case involved a denial of a claim for nonrestorative speech therapy for a child with autism covered by Raytheon’s self-insured group health plan. Plaintiffs in this case assert that that the exclusion only applied to a BH benefit and therefore violated parity. This is just one example of litigation in this area examining whether exclusions of a specific BH treatment or condition is permitted under MHPAEA.
3. Disclosure Rules
Federal parity law requires plans to disclose to plan enrollees upon request the criteria that is used by the plan to determine the medical necessity of BH treatment.22 The MHPAEA also required that plans provide the rationale for denying a BH claim to an enrollee.
Amendments to the parity law in the 2020 Consolidated Appropriations Act (CAA) now requires plans to prepare and provide an NQTL comparative analysis and make it available to the relevant government agency upon request.23
who enforces MHPAEA?
Enforcement of MHPAEA is overseen by several different federal and state agencies depending on the type of plan involved. Table 2 summaries the agencies involved and their enforcement methods.
| Table 2: MHPAEA Enforcement | ||
| Plan Type | Who Enforces? | Enforcement Tools |
| Private Employer-sponsored Group Health Plan (both insured and self insured): | DOL/Treasury |
|
| Non-Federal Employer-sponsored Group Health Plan (State and local government employer plan) | CMS |
|
| Individual insurance plan (on or off exchange) | State insurance agency/ CMS as federal fallback* |
|
| Small group insurance plan (on or off exchange) and large group insurance plan | State insurance agency/CMS as federal fallback |
|
| Medicaid plans | State Medicaid agency/CMS |
|
| NOTES: *”federal fallback” means CMS enforces when state does not substantially enforce the requirement. | ||
While DOL can investigate and enforce violations of the parity law for private employer plans, it does not have independent authority to assess a civil penalty specific to parity.24 It can refer cases to Treasury, which can assess a $100 a day penalty per affected individual for violations.25 A provision in ERISA26 prevents DOL from enforcing parity and other federal health insurance protections, in certain circumstances, directly against insurers. Unless the insurer functions as a “fiduciary” under the plan, DOL has limited ability to enforce most of ERISA’s health coverage provisions directly against these entities.27
CMS and state Medicaid agencies oversee compliance activity for federal Medicaid parity rules. States generally are responsible to determine whether the overall delivery system complies with the Medicaid/CHIP parity rule and make documentation available through a public posting and to CMS.28 States have other oversight tools as part of their contracts with managed care entities, such as performance guarantees (penalties assessed when specific contract requirements are not met).
Evidence of low parity compliance. Earlier this year, DOL, Treasury and the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) jointly issued a report to Congress on the current status of agency parity enforcement for non-Medicaid plans. The report raised alarms in its conclusion that in 2021 none of the NQTL comparative analysis submitted by employer-sponsored plans and insurers, upon initial agency review, contained information sufficient to meet the standards required under the parity law.29 According to the agencies, some plans were completing an NQTL comparative analysis for the first time in 2021 only in response to the agency request for the analysis. These plans had imposed NQTLs on BH benefits for years without performing a compliance assessment. Other plans provided a compliance analysis with limited information on the factors and evidentiary standards supporting use of specific NQTLs. For Medicaid plans, there is concern that few substantive changes were made in response to parity implementation. A 2021 report prepared by the Medicaid and CHIP Payment and Access Commission (MACPAC) concluded that implementation of MHPAEA had done little to substantially improve access to BH care for Medicaid and CHIP beneficiaries.
DOL recommends enforcement enhancements. The DOL has requested tools to expand its ability to enforce the law. The Department’s 2022 report to Congress includes proposals for legislative changes to improve their enforcement related to private employer-sponsored ERISA plans. DOL calls on Congress to amend ERISA30 to:
- Give DOL the authority to assess civil monetary penalties for MHPAEA violations
- Allow DOL to pursue “all appropriate actors” when enforcing the law, not just plan sponsors and others meeting the definition of fiduciary. This would include the third parties who design and implement BH benefits for employers. Third party administrators for large, self-insured employer plans, for example, are often the same insurance companies that provide fully insured coverage not only to employer plans, but in the individual and small group insurance market and in Medicaid managed care plans.
- Clarify that participants and beneficiaries who are harmed by a parity violation can seek relief to recover what they lost due to the violation. The parameters of this “make whole” relief is not specified in the report.
First federal litigation for parity violations. In August 2021 the DOL initiated its first litigation to enforce the parity law. In Walsh v. United Behavioral health (UBH), the agency alleged, among other issues, that UBH (acting as an ERISA fiduciary) reduced reimbursements for certain out-of-network non-physician BH providers, but did not do so for non-physician medical providers. The case was settled for $15 million, with UBH agreeing to take specific actions to address the NQTL. The settlement was done jointly by the DOL and the New York Attorney General.
Looking Ahead: Key Policy Issues
Implementation of federal BH parity protections is at an inflection point. As evidence of poor compliance increases, so have questions about whether the current standards are effective to address the issues. proposed legislation specific to BH parity is expected . Several pieces of pending legislation include parity changes, including legislation that recently passed the House that would remove the ability of self-insured state and local government plans to opt out of parity compliance and provide funding to states to enforce commercial parity rules. Other pending bills would increase DOL’s enforcement authority over parity through additional civil penalties and other enforcement features.31
Key issues raised by both advocates and regulators include:
Simplifying standards. Parity standards are solely based on a comparison of BH benefits to what is provided for medical benefits by each plan. These comparisons are often challenging to make given the differences between BH care and medical care, where apples-to-apples comparisons are sometimes difficult. Also, since MHPAEA does not require coverage of any specific BH service, these comparisons will differ from plan to plan, making the comparison even more complicated and resource intensive. Federal regulators in their 2022 Enforcement Report to Congress suggested that the use of more objective and uniform national standards as part of MHPAEA may strengthen BH coverage and provide clearer rules that consumers can understand and that will apply regardless of the type of health coverage or the state where they live. Developing external benchmarks that are at a minimum based on nationally recognized standards of care and that change as the evidence base evolves is one possible policy direction. For example, a uniform approach to determining what covered items and services are considered BH versus medical would simplify the required comparative analysis.
Taking a closer look at medical management criteria. The Wit case and similar litigation shines a light on the medical necessity criteria used to make BH coverage decisions. Some states, such as California, now have laws that require insurers use independent criteria developed by a nonprofit to determine medical necessity for BH claims. The federal parity law, however, does not include equivalent standards or require plans to develop coverage criteria based on generally accepted standards of care. Closer scrutiny of the medical management techniques applied to BH claims may take place because of this litigation. For instance, the DOL’s first parity litigation involved use of alleged arbitrary thresholds for utilization review of certain psychotherapy treatment.
Assessing how parity can address network adequacy challenges. Evaluating what an adequate BH network of providers looks like, one that addresses the full spectrum of BH needs from screening to inpatient services, will be key to developing a standard that can be enforced. This will likely involve looking at existing networks and the disparate number of in-network BH providers, not simply the processes involved in developing the network that is the current focus of NQTL review. Phantom networks, where providers listed in the network directory are no longer taking new patients, is a particular problem for accessing BH services.
Development of a common approach to assess BH network adequacy may be useful. New regulatory standards for the federal marketplace will include time-distance access standards for BH providers, as well as appointment wait time standards for BH visits. CMS regulations do require states to set a quantitative network adequacy standard for Medicaid managed care plans and the agency has developed a toolkit for states to use in monitoring BH network adequacy. For Medicaid, network adequacy standards will differ from state to state, and a recent study found that care may still be concentrated among a small number of providers even where quantitative network adequacy standards apply. Similar network adequacy initiatives could focus on large, self-insured employer plans, who currently do not have any network adequacy requirements under parity or any other federal law.
Use of telehealth is an important part of improving access. An additional part of the inquiry is looking at access problems that cannot be addressed through telehealth alone, including treatment for those with serious mental illness. Finally, where the provider shortages in certain areas mean plans cannot meet a network adequacy standard for BH, some mechanism for patients to obtain out-of-network care at in-network rates may be important.
Evaluating enforcement tools. The limited compliance with parity standards might be improved by giving the agencies more mechanisms to hold plans accountable; and by exercising current regulatory authority in different ways.
With respect to coverage decisions, additional data reporting could inform oversight of how plans cover BH services compared to other claims. Federal transparency data reporting, enacted as part of the ACA in 2010, requires private health plans, including employer sponsored plans, to periodically report data to the federal government related to how coverage works in practice. Among other things, the law requires plans to report data on claims denials. To date this requirement has been implemented on a limited basis for nongroup plans in the federal marketplace, and not at all for employer-sponsored plans. For Medicaid plans, CMS and states might be able to use their existing oversight authority to require this type of data reporting.
Finally, enforcement enhancements that create incentives for plan sponsors to perform program oversight of their BH coverage is another option being evaluated. Employers, for example, may be limited in their ability to self-monitor compliance unless third party insurers and other entities that administer their plans share information about how they design and manage BH benefits. More emphasis on data sharing with vendors so employer plan sponsors can perform their monitoring role might improve compliance. CMS and state Medicaid agencies, by contrast, have oversight responsibilities under Medicaid parity rules, along with documentation requirements for public disclosure of the comparative analysis. They may already have the ability to access information from MCOs and other entities and can utilize this authority to enhance their parity enforcement.
These possible changes to BH parity come at the same time as concerns about a BH workforce shortage and other structural problems in the delivery of BH care that will impede progress even if BH coverage is expanded. Also, there are always tradeoffs between increased costs versus broader BH coverage that will be important to consider as existing BH medical management practices are reevaluated.
This work was supported in part by Well Being Trust. KFF maintains full editorial control over all of its policy analysis, polling, and journalism activities.
Appendix
| Appendix Table 1: Major Differences – Commercial MHPAEA v. Medicaid MHPAEA | ||
| Topic | Commercial | Medicaid |
| Definition of behavioral health | Plans define what is considered behavioral health versus medical care. | State Medicaid agencies can define what is behavioral health versus medical care. MCOs, PHIPs and PAHPs must follow the state’s definition. |
| Long term care services | Long term care services are considered “excepted benefits” that do not have to comply with parity. | Long term care services generally must meet parity standards. |
| Out-of-network classifications | Plans must evaluate parity for out-of-network inpatient care and out-of-network outpatient care. | The two out-of-network classifications do not apply to Medicaid MHPAEA. |
| Network tiers | Plans can determine parity separately for each provider network tier in a classification. | Medicaid parity regulations do not give Medicaid plans with network tiers the ability to evaluate parity within each tier. Parity is evaluated for all care within a classification. |
| Cumulative Quantitative Treatment Limits | Quantitative treatment limits (such as a limit on the number of visits for a service per year) cannot accumulate separately for behavioral health and medical. | Quantitative treatment limits can accumulate separately for behavioral and medical services if certain standards are met. |
| Disclosure of reasons for denial of a claim | Plans subject to ERISA must provide the denial reason in the form/manner included in ERISA claims review rules that are separate from commercial parity rules. NonERISA plans that follow this form and manner are deemed to comply with this parity requirement. | Medicaid is subject to its own form/manner notice standards for providing the reason for a claim denial in adverse action notice regulations that are separate from Medicaid parity rules. |
| Cost exemption | Plans can qualify for a temporary exemption from meeting the MHPAEA standards if they meet certain requirements for cost increases. | Medicaid regulations do not apply the cost exemption to Medicaid. |
| SOURCE: 70 Federal Register 68240-68296; 80 Federal Register 18390-18445 | ||
Endnotes
- Behavioral health care includes any medication or service used to treat a mental health and/or substance use disorder and would include conditions and treatment for developmental disabilities such as autism. ↩︎
- Development of a bipartisan package of legislative reforms on various aspect of behavioral health care concerns is underway in both chambers of Congress. The Senate Finance Committee issued a Request for Information in 2021 and in March 2022 released a report, Mental Health Care in the United States: The Case for Federal Action, that includes a discussion of mental health parity. https://www.finance.senate.gov/chairmans-news/finance-committee-releases-bipartisan-report-on-mental-health-care-in-america- ↩︎
- Parity applies regardless of status as a grandfathered or nongrandfathered plan if the plan covers BH. ↩︎
- Plans can opt out annually using a process administered by CMS. 42 U.S.C. § 300gg-21(a)(2). According to the last CMS posted list, over 200 nonfederal plans have opted out of compliance with MHPAEA. ↩︎
- ABPs are an alternative to the traditional Medicaid state plan benefit package and are based on private insurance designs. States can generally choose to offer ABPs but are required to offer them to newly eligible adults if the state expands Medicaid to this population under the ACA. The Medicaid parity rules do not apply to other Medicaid covered BH services that are provided fee-for-service although CMS encourages states to apply parity protections to those services. ↩︎
- Variations in how MHPAEA applies to Medicaid expansion CHIP programs, separate CHIP programs and programs that are a combination of both are described in section 8 of the CMS Parity Compliance Toolkit Applying Mental health and Substance Use Disorder Parity Requirements to Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Programs (January 2017), pp. 57-58. https://www.medicaid.gov/sites/default/files/2019-12/parity-toolkit.pdf ↩︎
- This means that parity does not apply to Medicare Part A, B or D services covered by Medicaid MCOs through integrated plans for dual eligible (Medicare and Medicaid) beneficiaries. 61 Federal Register 18424 (March 30, 2016). ↩︎
- 29 U.S.C. § 1185a(c)(2). Federal agencies have not indicated whether any plans have applied for this exemption. ↩︎
- The EHB benchmark choices are (1) any of the three largest state employee plan health benefit options, (2) the largest plan in any of the three largest small group insurance market products, (3) any of the three largest national Federal Employee Health Benefit Program (FEHBP) national plan options, and (4) the coverage offered by the largest insured commercial non-Medicaid HMO in the state. 45 C.F.R. § 156.100. ↩︎
- The IMD exclusion prohibits Medicaid payment for services for adults aged 22 to 64 in institutions with more than 16 beds that are primarily engaged in behavioral health treatment. While this might be considered a limitation on coverage that must be compared with limits on medical benefits in the inpatient classification under MHPAEA, CMS did not include this as part of their Medicaid MHPAEA regulation. Despite the exclusion, some states use Section 1115 waivers and other options to finance IMD services. Kaiser Family Foundation, State Options for Medicaid Coverage of Inpatient Behavioral Health Services (November 2019) https://modern.kff.org/medicaid/report/state-options-for-medicaid-coverage-of-inpatient-behavioral-health-services/ ↩︎
- 75 Federal Register 5412 (February 2, 2010). ↩︎
- CMS, Parity Compliance Toolkit Applying Mental health and Substance Use Disorder Parity Requirements to Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Programs, pp. 10-15. ↩︎
- 42 C.F.R. §§ 438.910(c)(4), 440.395(b)(3)(iv). ↩︎
- 81 Federal Register 18398-9 (March 30, 2016). ↩︎
- Separate dollar limits can apply to BH and medical/surgical benefits but more restrictive limits on BH are prohibited. For example, if an annual aggregate dollar limit applies to less than two-thirds of expected payments for medical/surgical benefits in a year, plans cannot impose any annual aggregate dollar limit on BH benefits in a year. ↩︎
- 45 C.F.R. § 146.136(c)(4)(ii); 42 C.F.R. § 438.910(d)(2) ↩︎
- DOL, Treasury and HHS, 2022 MHPAEA Report to Congress (January 2022) p. 34 ↩︎
- DOL, Treasury and HHS, FAQs About Mental Health and Substance Use Disorder Parity Implementation & the 21st Century Cures Act Part 39 (FAQs Part 39), Question 7 (September 5, 2019). https://www.dol.gov/sites/dolgov/files/EBSA/about-ebsa/our-activities/resource-center/faqs/aca-part-39-final.pdf ↩︎
- FAQs Part 39, Question 6. ↩︎
- 45 C.F.R. § 146.136 (definition of “treatment limitation”) ↩︎
- FAQs Part 39, Question 4. ↩︎
- A model disclosure request form was developed to facilitate enrollee requests for this information as well as information on a plans’ comparative analysis of NQTLs. The form is optional for plans to use and was created by DOL and the other agencies who implement the non-Medicaid parity rules. ↩︎
- Medicaid plans are generally deemed to comply with these CAA rules if they met certain disclosure requirements in Medicaid parity regulations. In 2017, states had to document similar parity analysis and post it publicly on a website for benefits provided to Medicaid managed care enrollees. Similar documentation rules apply to Medicaid Alternative Benefit Plans. 42 CFR § 438.920; 42 CFR § 440.396. ↩︎
- Separate from MHPAEA, DOL can assess civil penalties in other circumstances, such as a failure of a plan sponsor to disclose certain information to a participant upon request (such as medical necessity criteria). DOL also has other enforcement tools under ERISA to bring actions against those who are “fiduciaries” under ERISA. An ERISA fiduciary is any entity that has discretionary authority or control of a plan’s management or administration or the disposition of plan assets. Who is a fiduciary is often very fact specific, subject to evolving case law, and has generally left out the entities that design and control the key factors that determine what health benefits are covered. ↩︎
- It is not clear whether Treasury has ever assessed a penalty using this authority. According to a 2019 General Accountability Office (GAO) report on parity enforcement, the DOL has never referred a case to Treasury to assess a penalty. GAO, State and Federal Oversight of Compliance with Parity Requirements Varies (December 2019) (GAO Parity Enforcement Report), p. 25 https://www.gao.gov/assets/gao-20-150.pdf ↩︎
- 29 USC § 1132(b)(3). ↩︎
- Insurers are often the third-party administrators (TPA) of self-insured plans and are the entities that design and implement behavioral health benefits, build provider networks, and oversee medical management structures. Employers often adopt the TPA’s prototype plan as is with limited changes. These TPA activities are not always defined by courts as ERISA fiduciary functions. ↩︎
- CMS, Frequently Asked Questions: Mental Health and Substance Use Disorder Parity Final Rule for Medicaid and CHIP, Q7 and Q8 (March 29, 2016). https://www.medicaid.gov/sites/default/files/2019-12/faq-cms-2333-f.pdf ↩︎
- A 2019 GAO report on parity enforcement for commercial plans concluded that the extent of parity compliance was unknown and that agency reliance on targeted reviews based on complaints and other information may not be adequate to assess compliance. GAO Enforcement Parity Report, (December 2019). ↩︎
- These three changes are also included in President Biden’s Fiscal Year 2023 Budget. https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/budget_fy2023.pdf. The House-passed Build Back Better legislation from 2021 also included these three changes. https://www.congress.gov/bill/117th-congress/house-bill/5376/text. ↩︎
- The House-passed Build Back Better legislation from 2021 would have given the DOL the authority to assess civil penalties for parity violations. This is similar to legislation introduced in 2021, H.R. 1364, the Parity Enforcement Act of 2021. https://www.congress.gov/bill/117th-congress/house-bill/1364/text. H.R. 7780 would make additional changes to ERISA’s enforcement scheme. https://www.congress.gov/bill/117th-congress/house-bill/7780/cosponsors?r=1&s=1 ↩︎