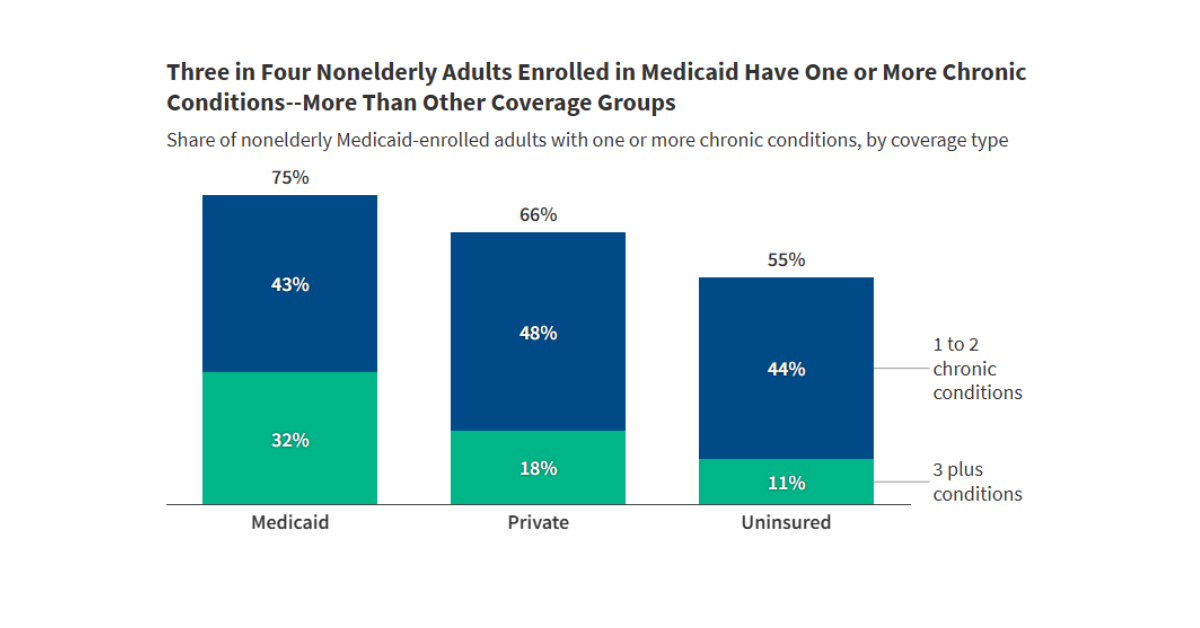
What is the Medicaid Hardship Exception and How Could it Affect Who’s Required to Work?
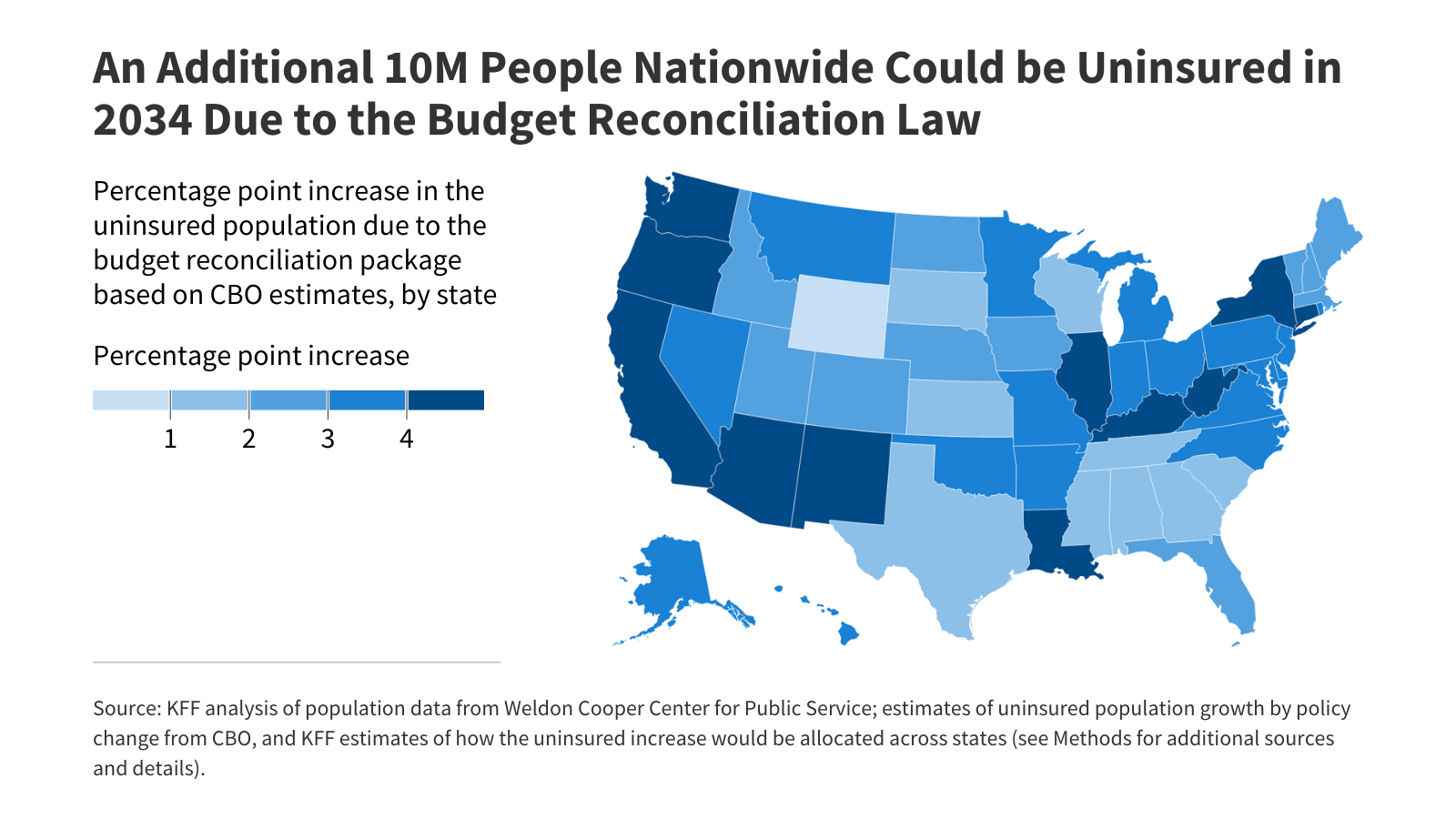
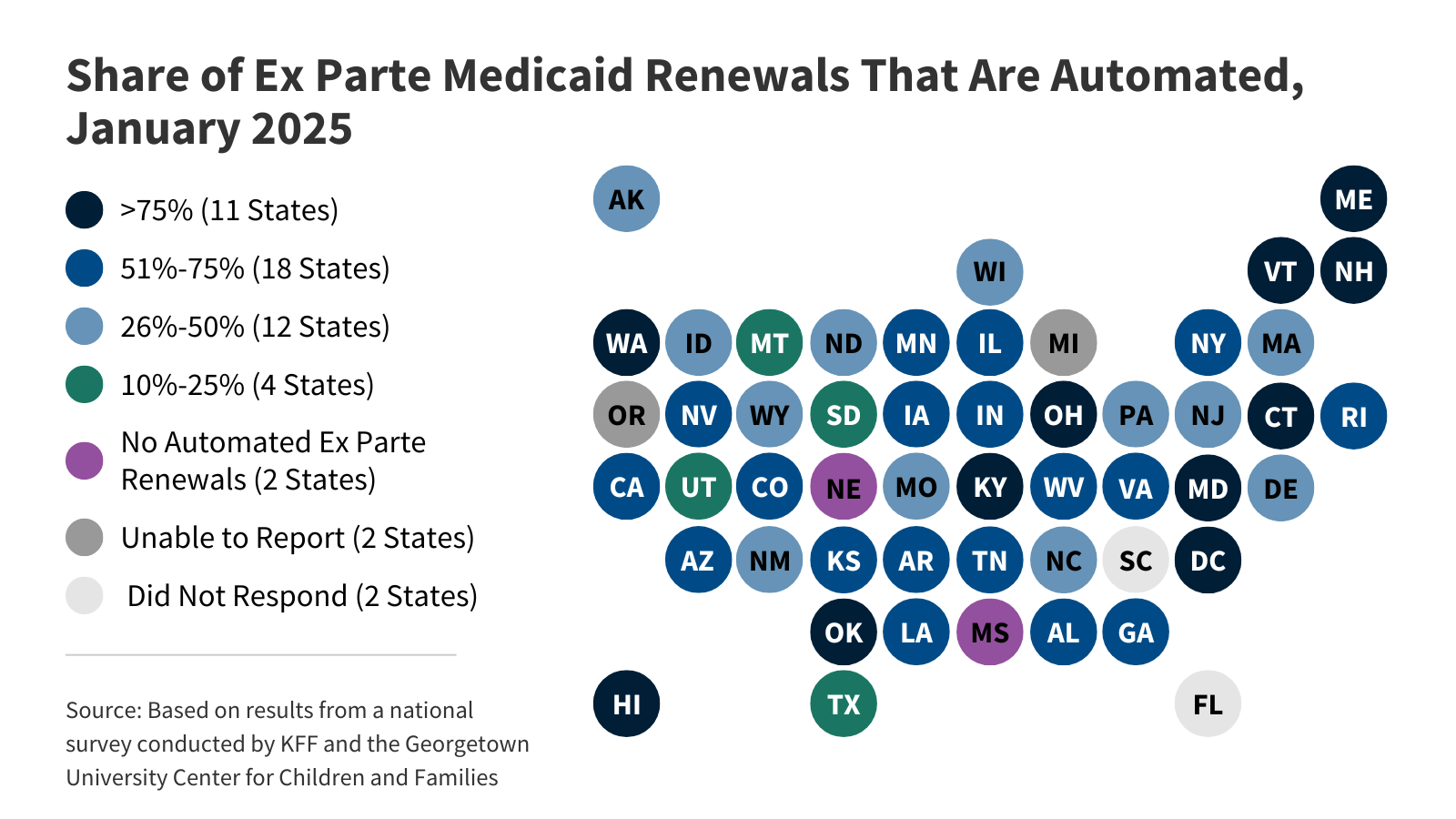
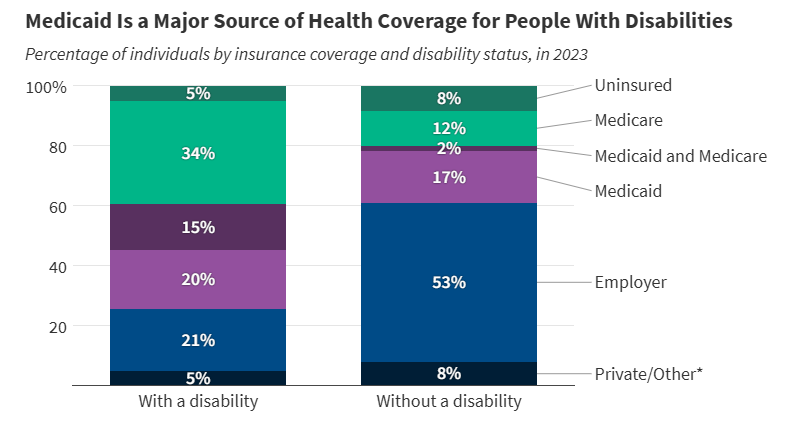
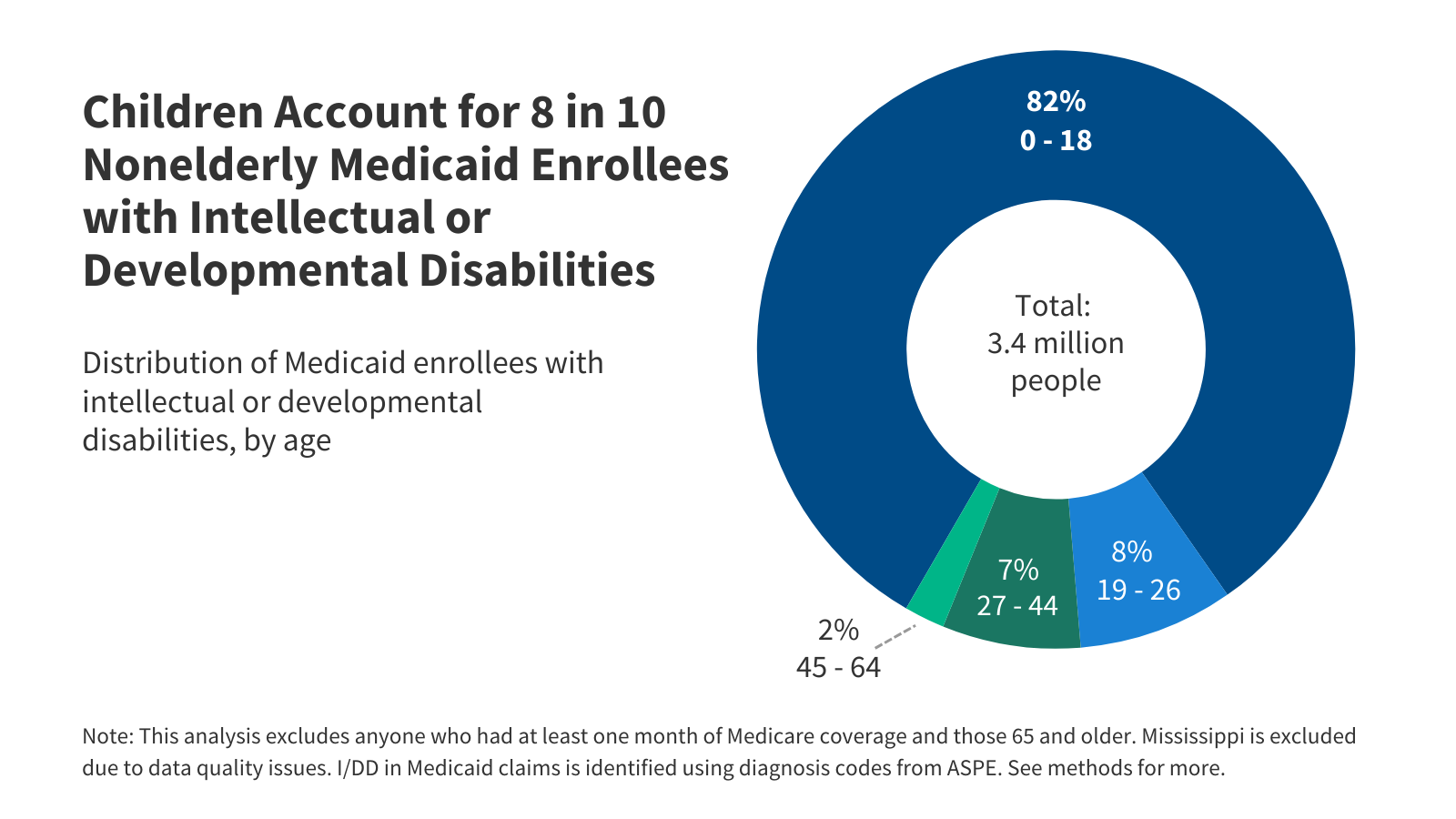
The number of Medicaid expansion enrollees who ultimately qualify for the high unemployment hardship exception will depend on how the exception is implemented and how unemployment rates changes.