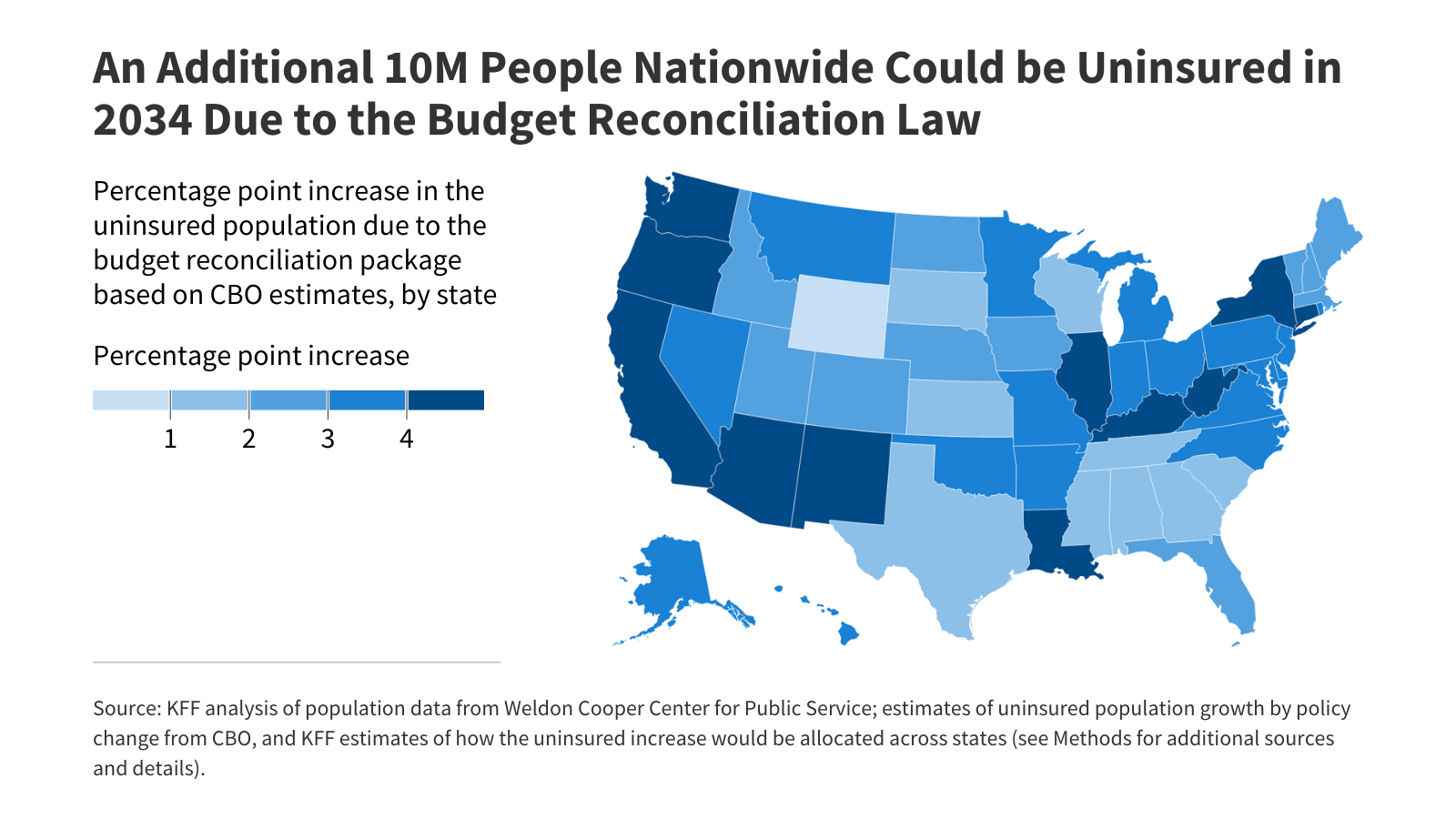
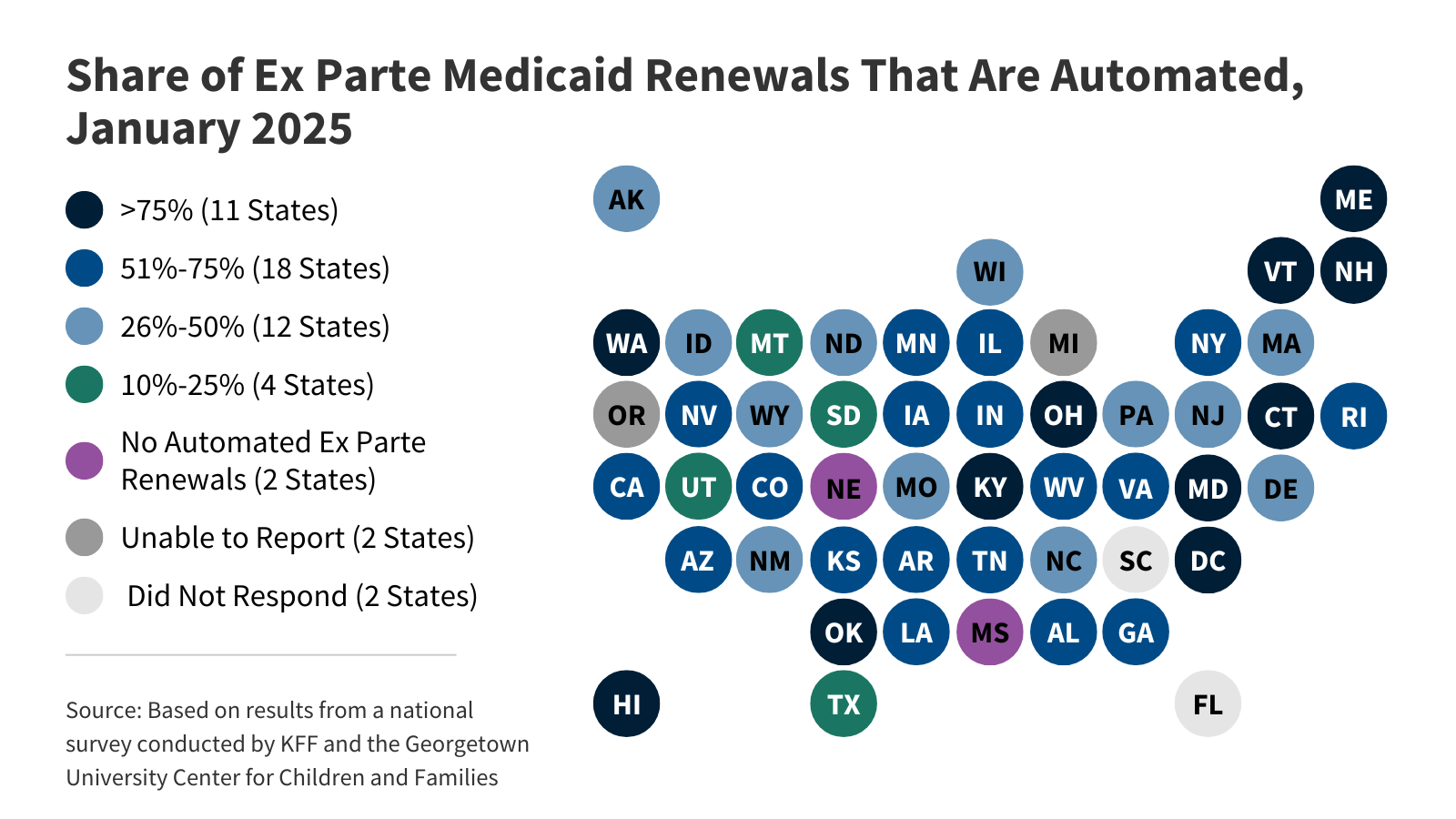
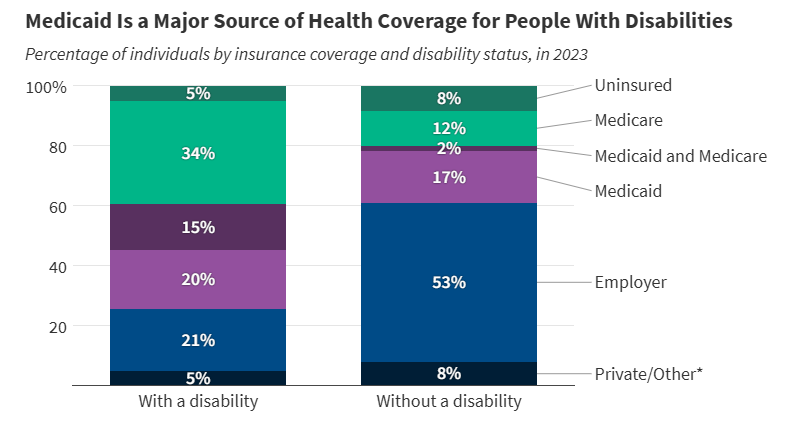
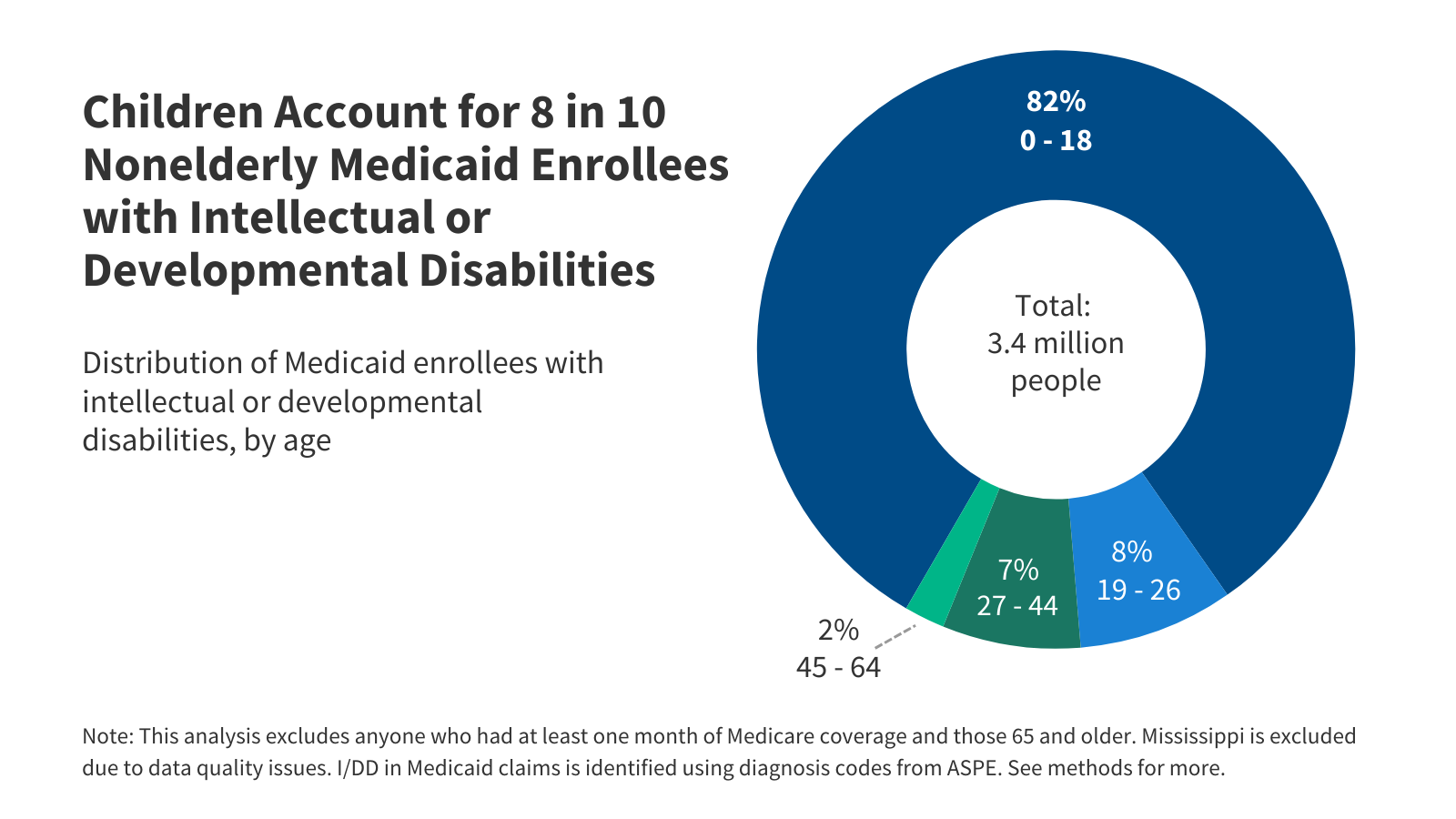
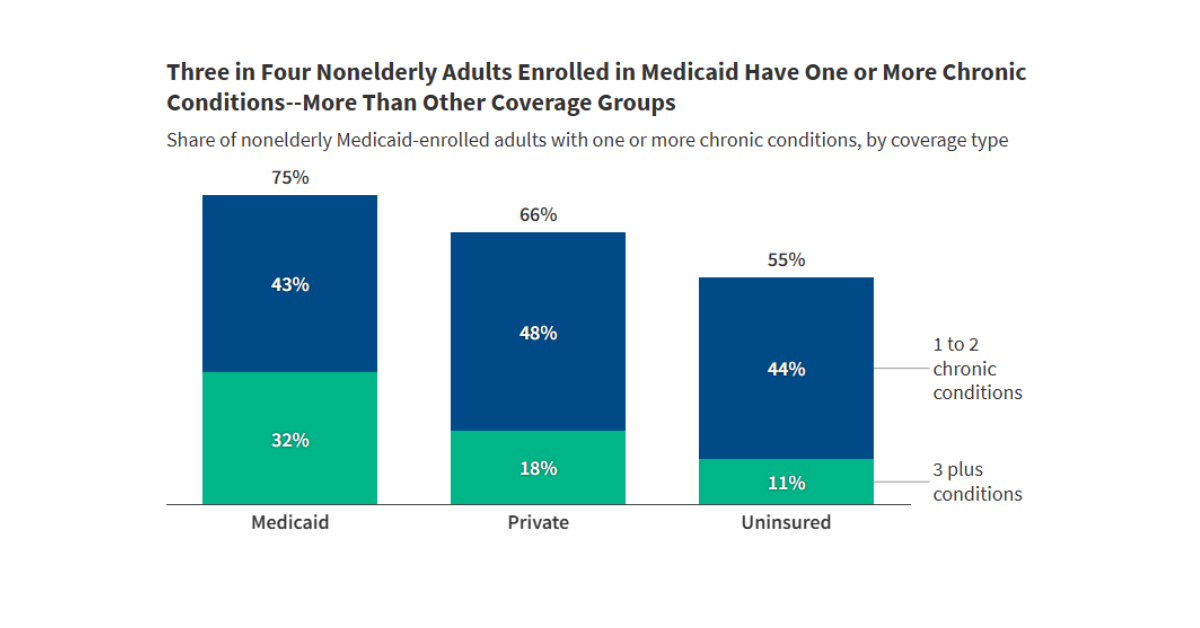
Wonk Shop: How Will States Implement Medicaid Work Requirements?
Four experts, including two state Medicaid directors, joined Health Wonk Shop moderator Larry Levitt in an hour-long discussion of how states will go about implementing new Medicaid work requirements.