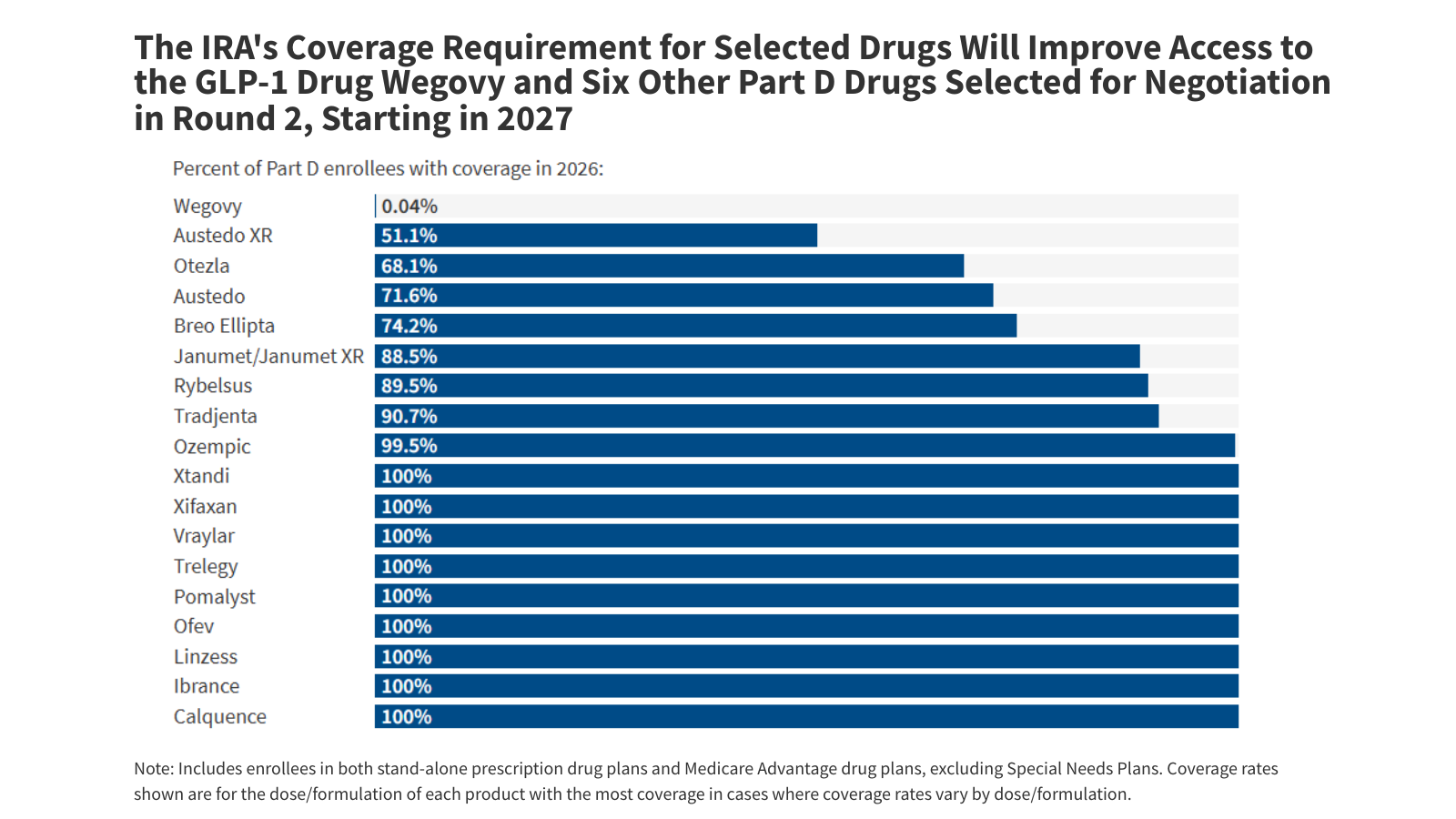
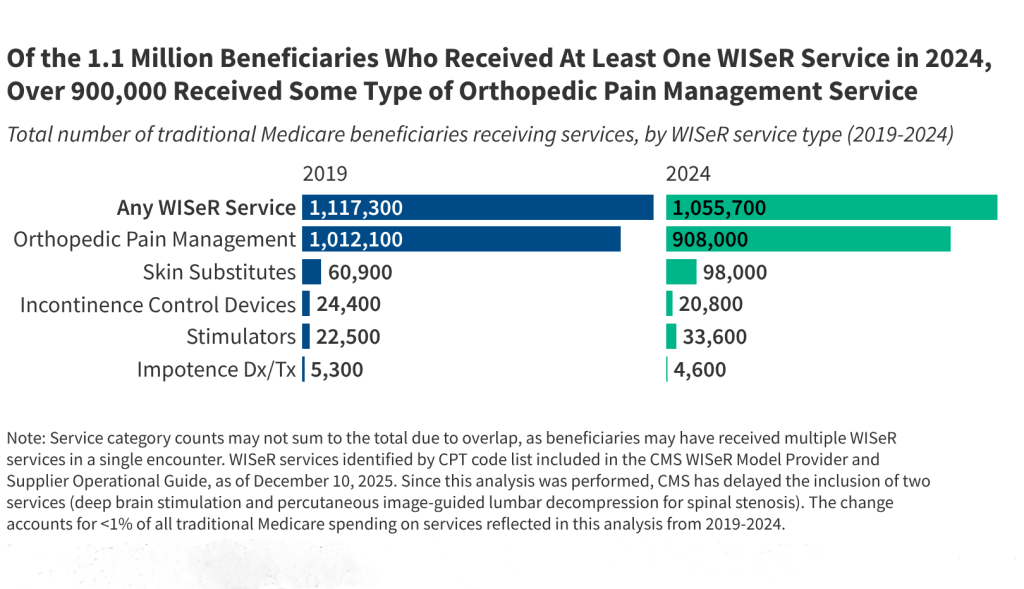
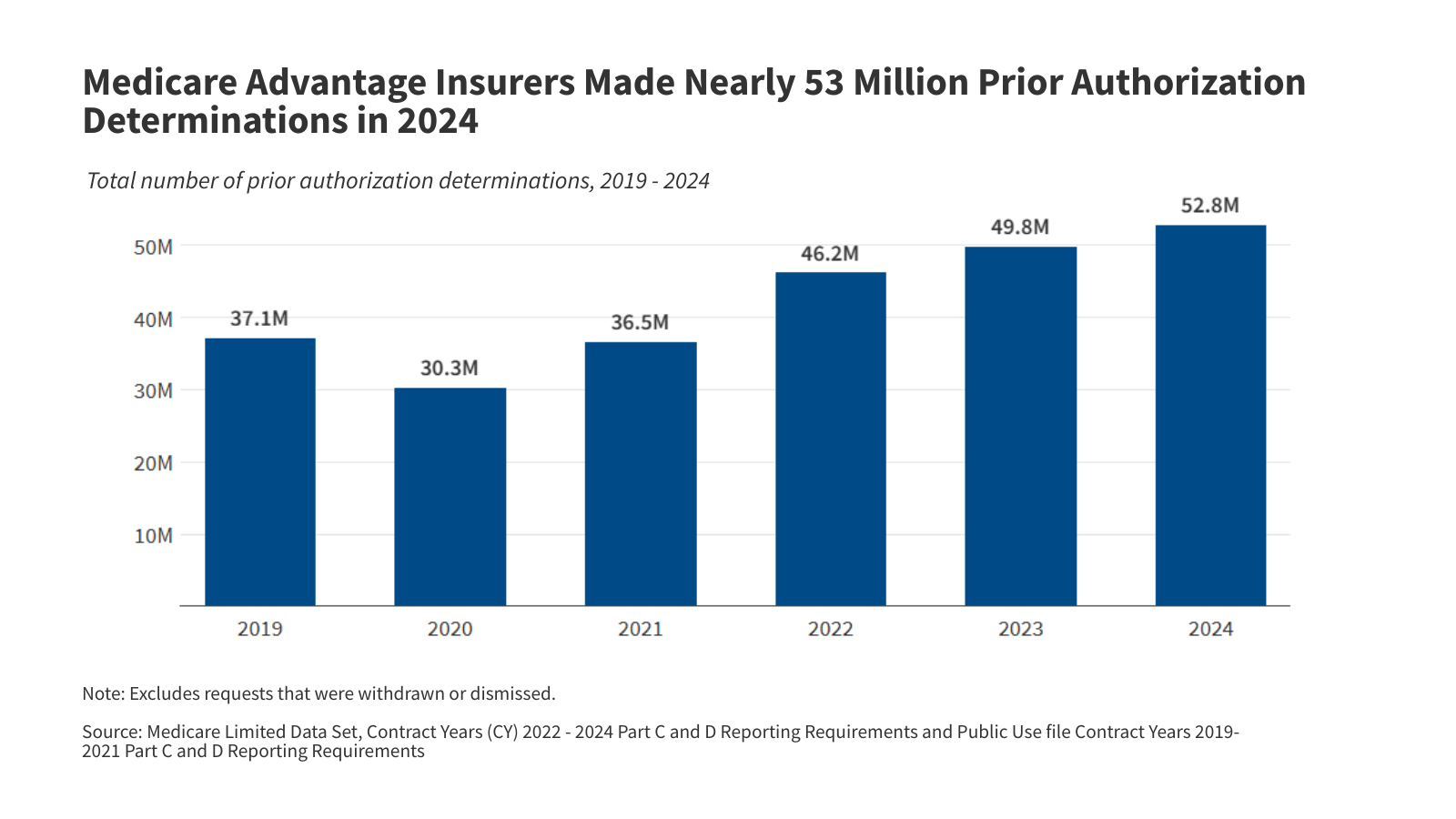
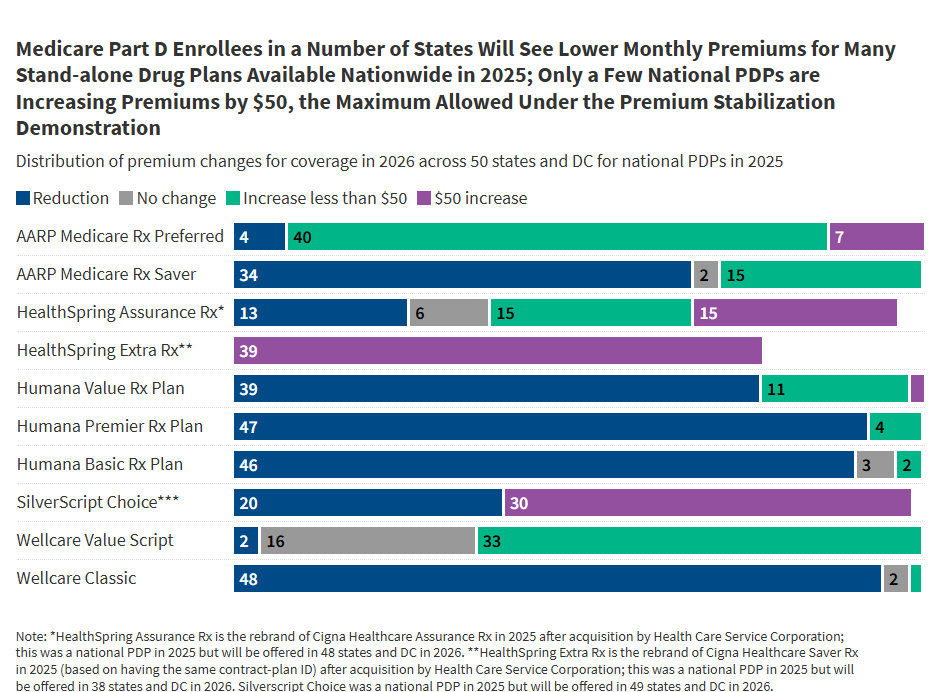
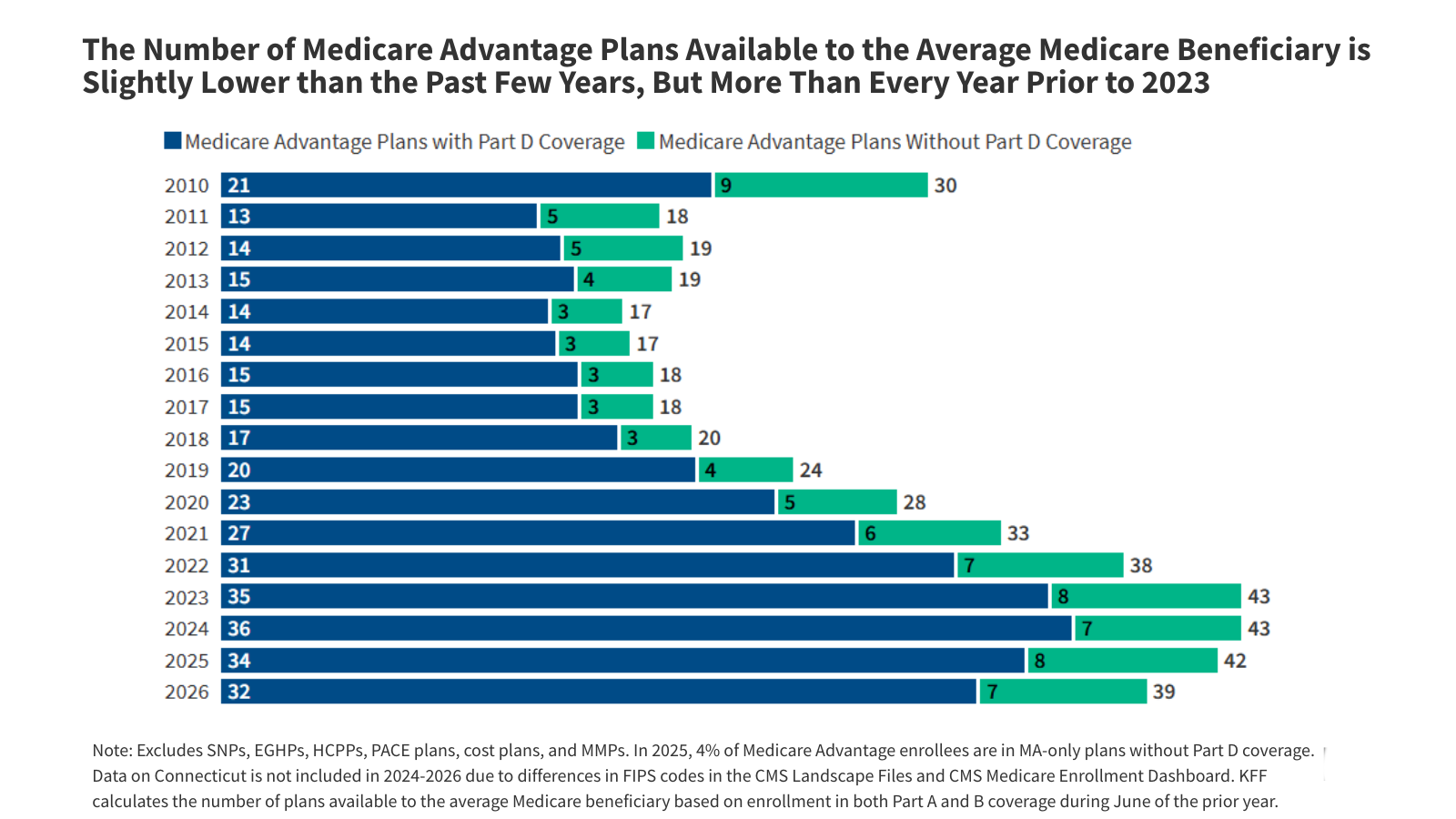
What Could the Health-Related Provisions in the Reconciliation Law Mean for Older Adults?
On July 4, President Trump signed into law the budget reconciliation bill, previously known as “One Big Beautiful Bill Act.” The law includes several policy changes that could have significant implications for the health and health coverage of older Americans ages 50 and older, including those who are covered by Medicare.