Challenges with Implementing Work Requirements
Many states are anticipating a variety of implementation challenges, including the need for complex system changes, a compressed implementation timeline, and limited staff capacity.
The independent source for health policy research, polling, and news.
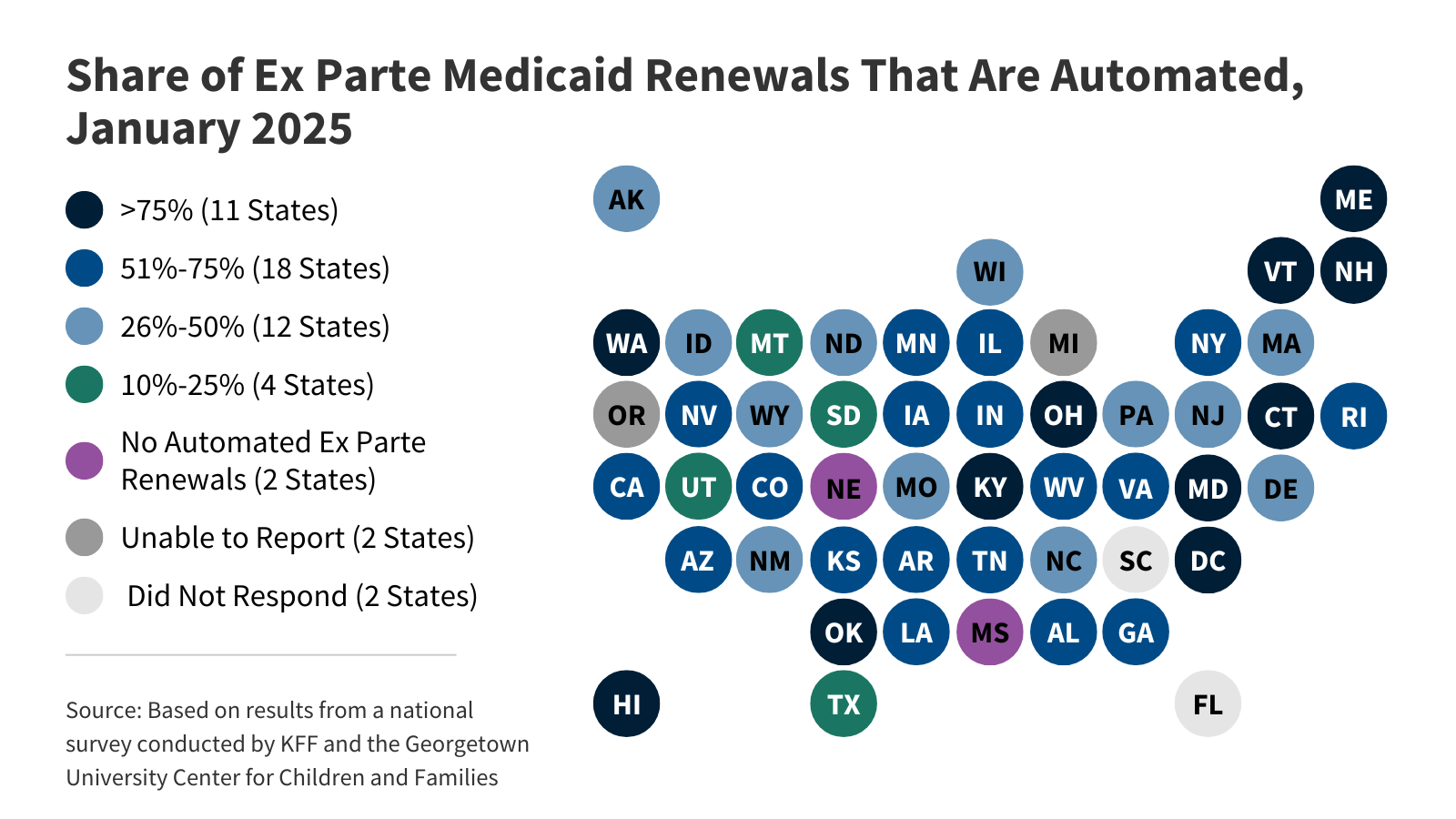
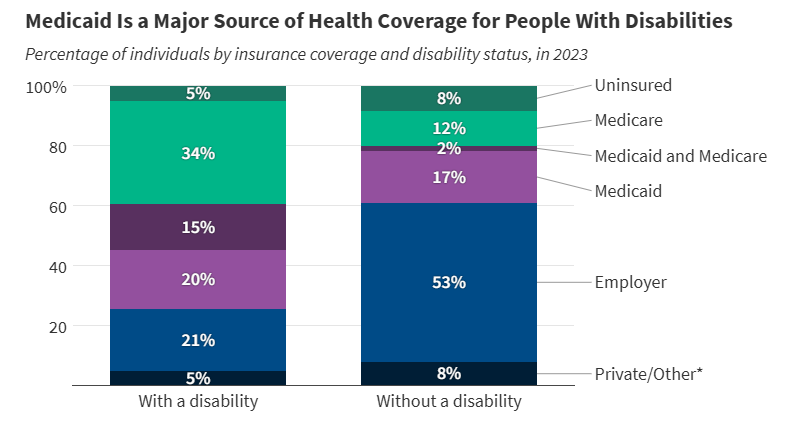
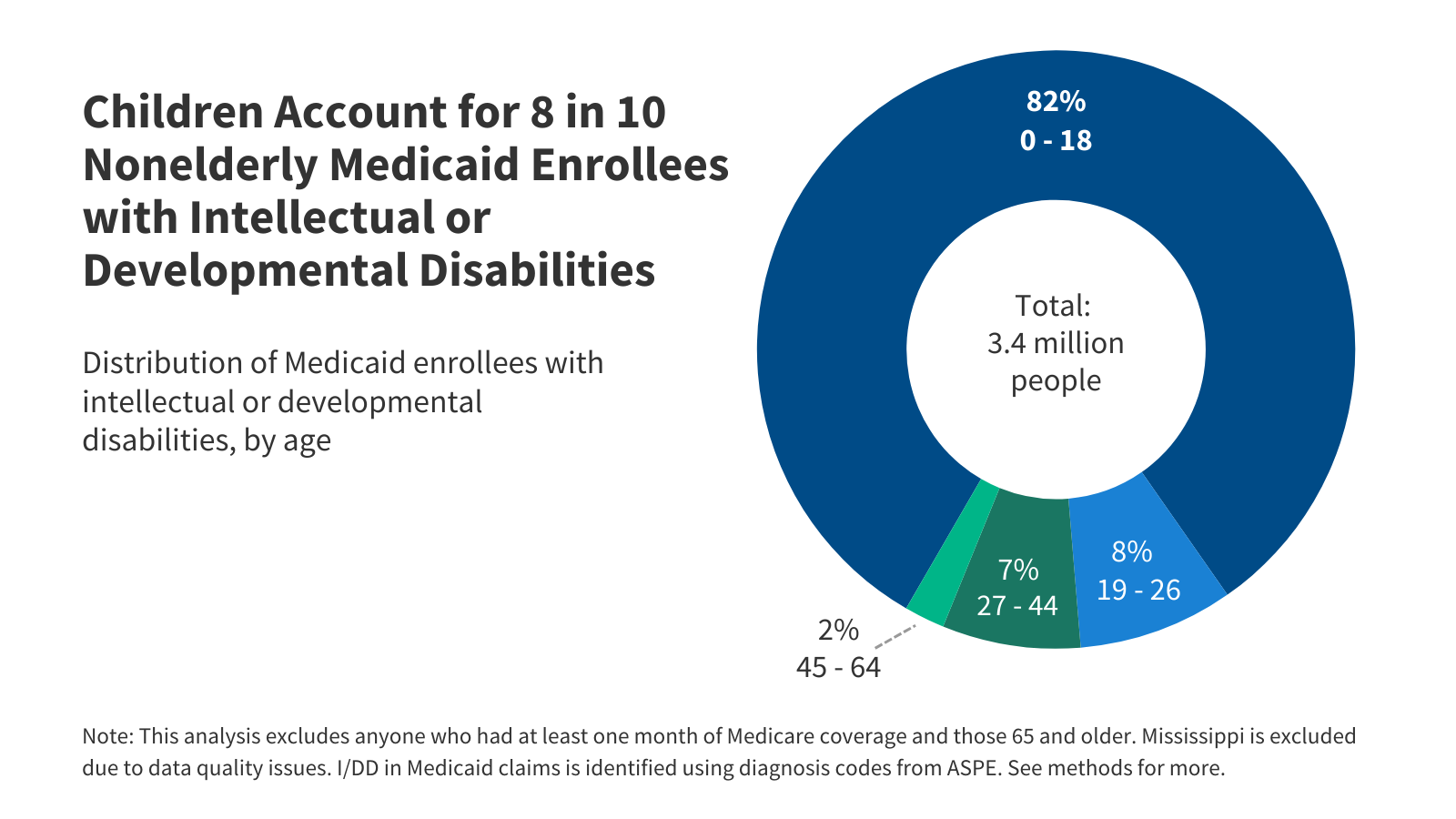
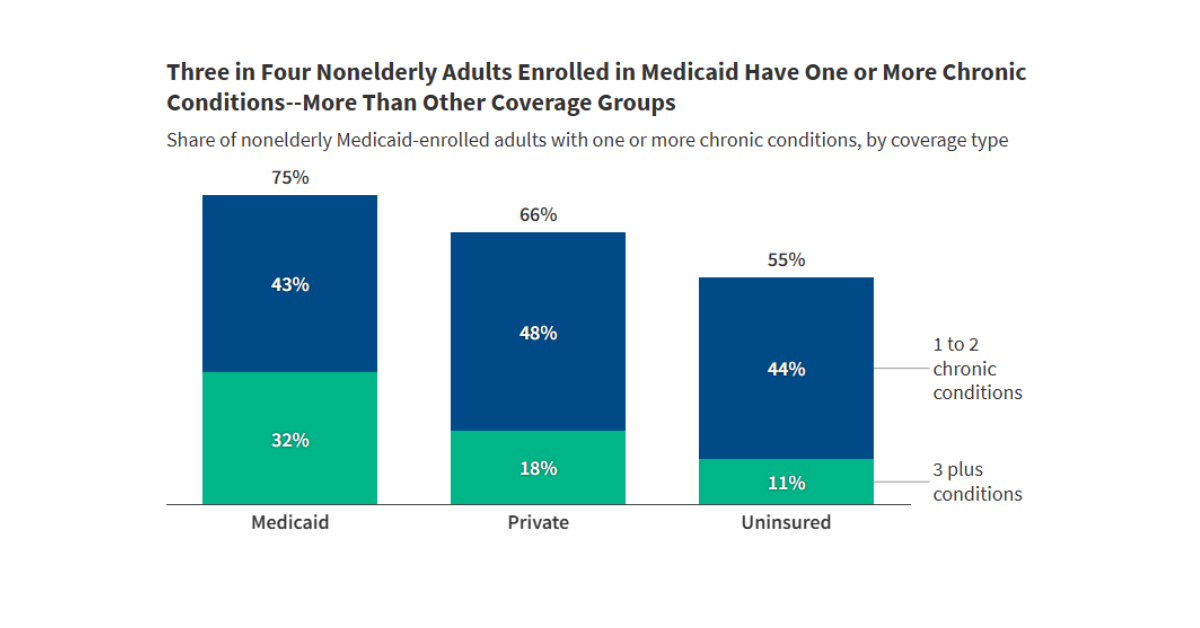
KFF’s interactive tracks key data and policies that will affect how states implement Medicaid work requirements, which are required under the 2025 budget reconciliation law starting in January 2027. The tracker includes state-level data on Medicaid enrollment and renewal outcomes as well as current state enrollment and renewal policies.
Medicaid enrollment fell 7.6% in FY 2025 and is expected to be largely flat in FY 2026. At the same time, total Medicaid spending grew by 8.6% in FY 2025 and is expected to grow by 7.9% in FY 2026.




Choose which emails are best for you.
Sign up here