Poll: Health Care Costs, Expiring ACA Tax Credits, and the 2026 Midterms
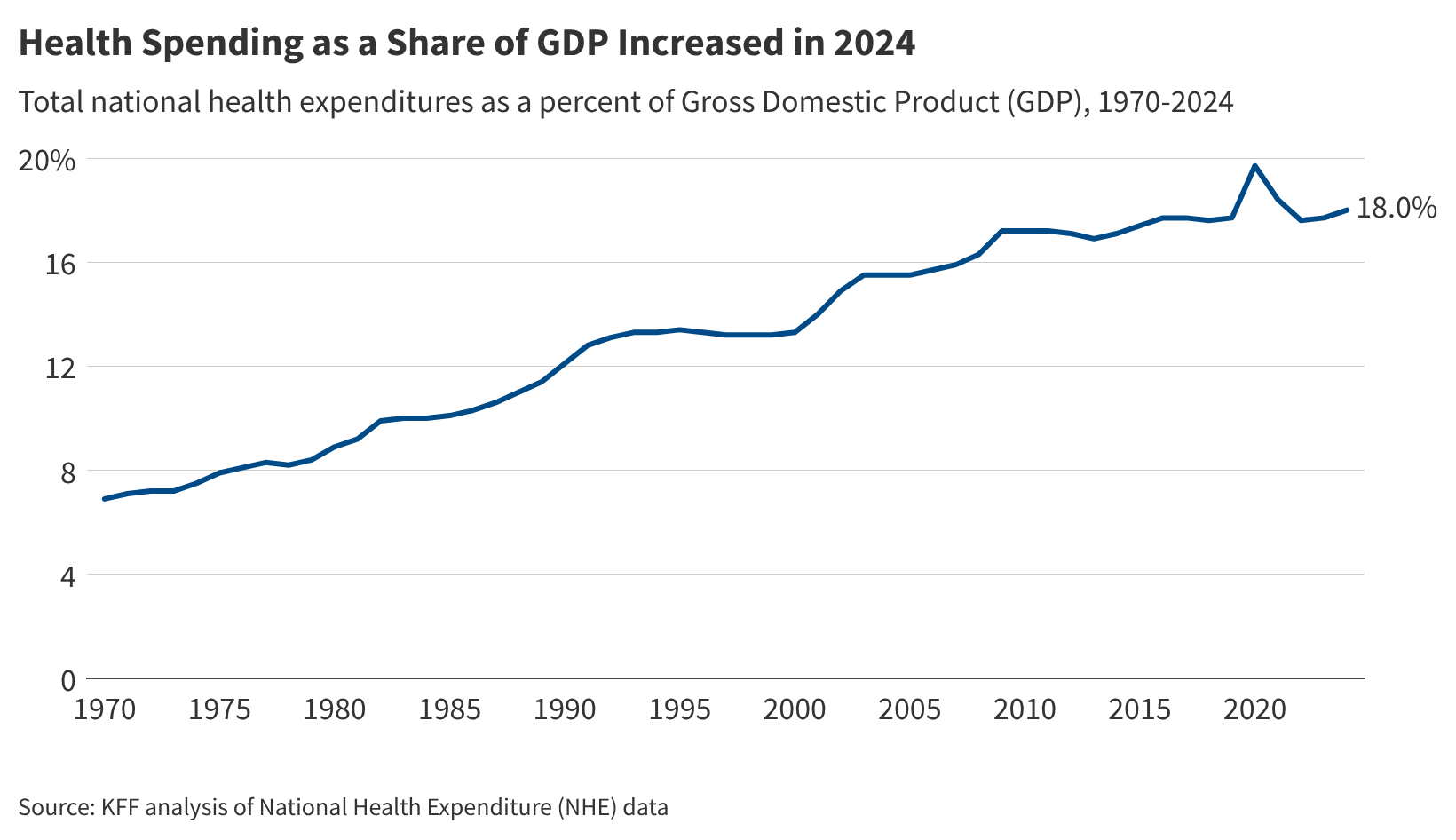
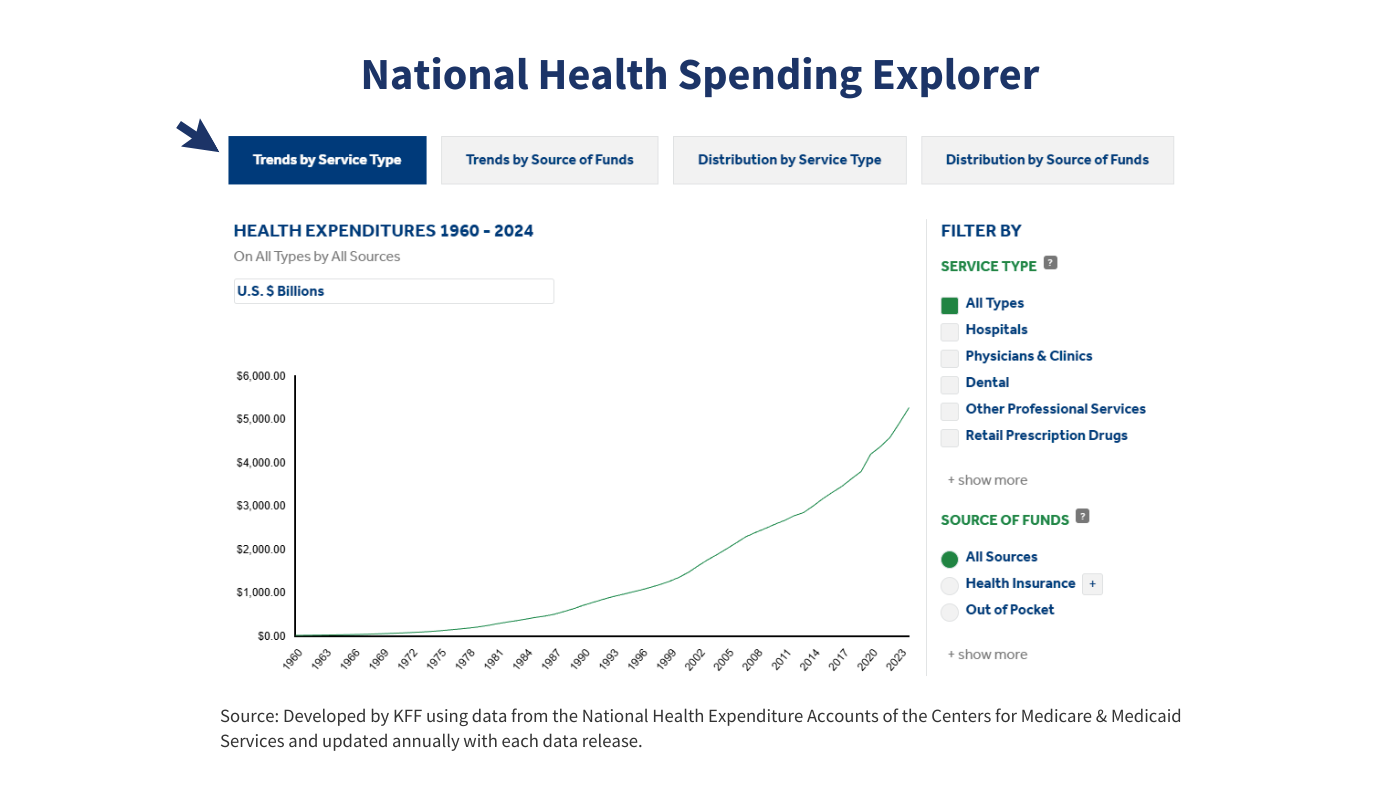
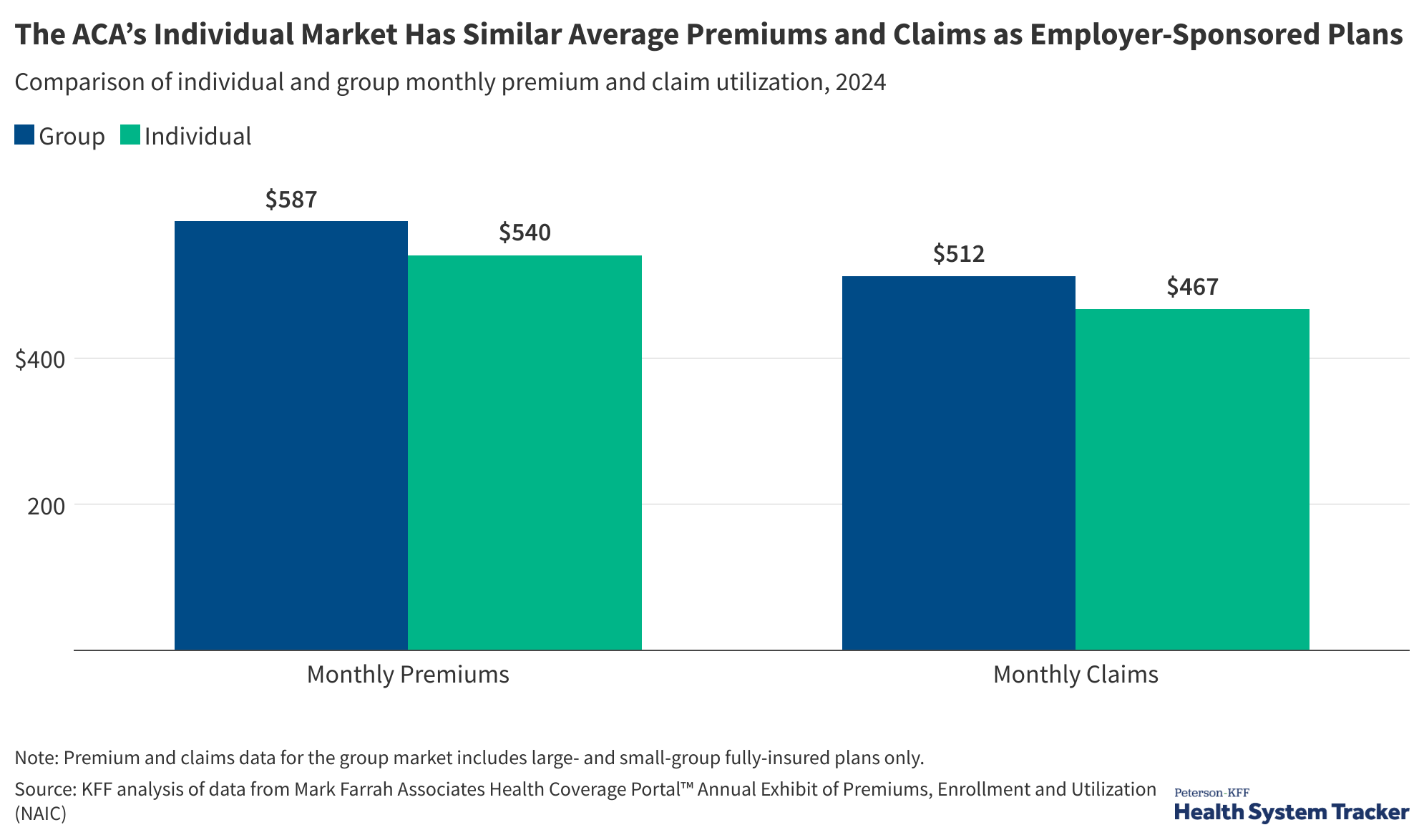
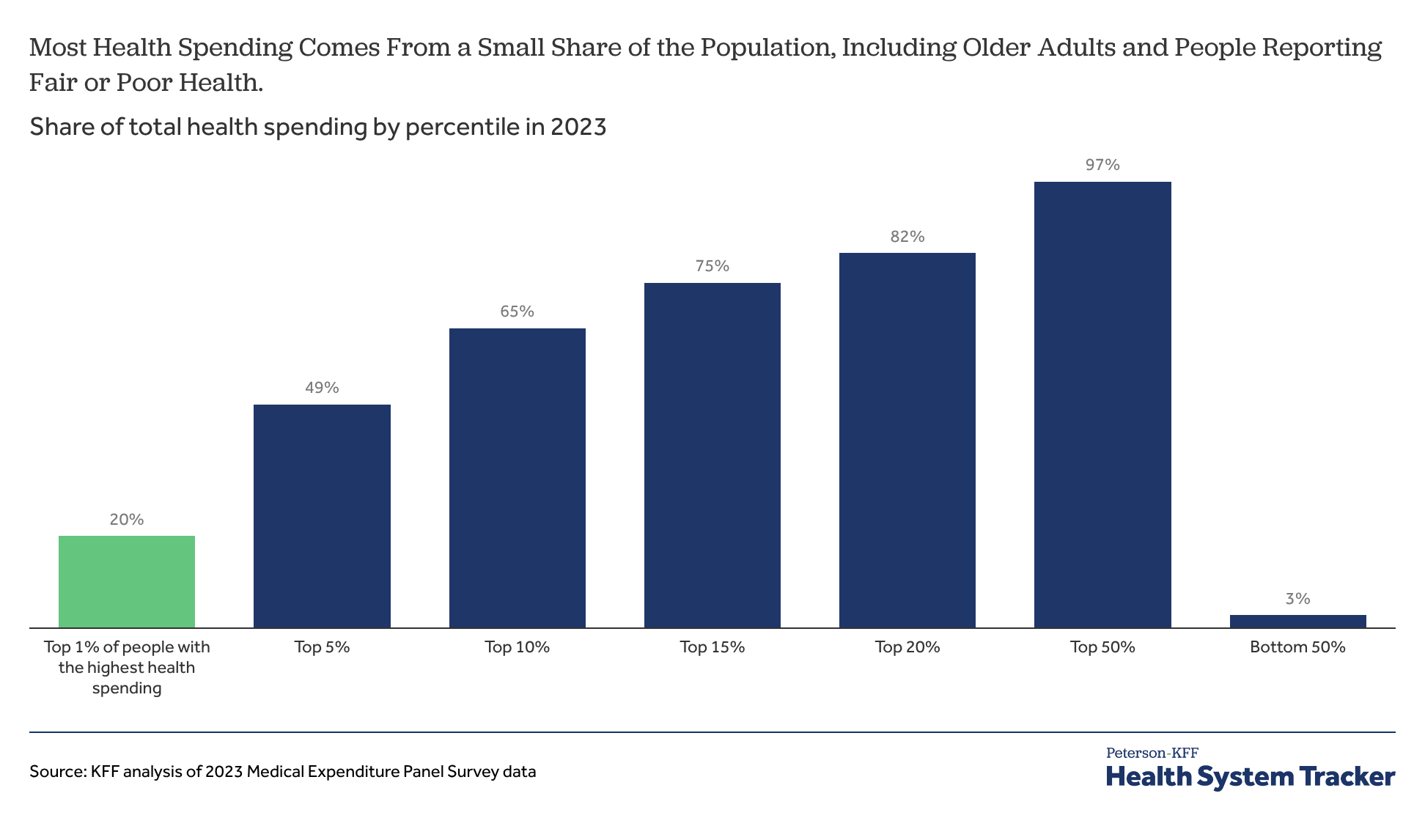
Heading into this midterm election year, the cost of health care tops the public’s economic anxieties, and more than 4 in 10 voters say the issue will have a major impact on their vote, a new KFF Health Tracking poll finds. Two thirds of public say Congress "did the wrong thing" by not extending ACA enhanced tax credits, but Republicans largely say Congress “did the right thing.”