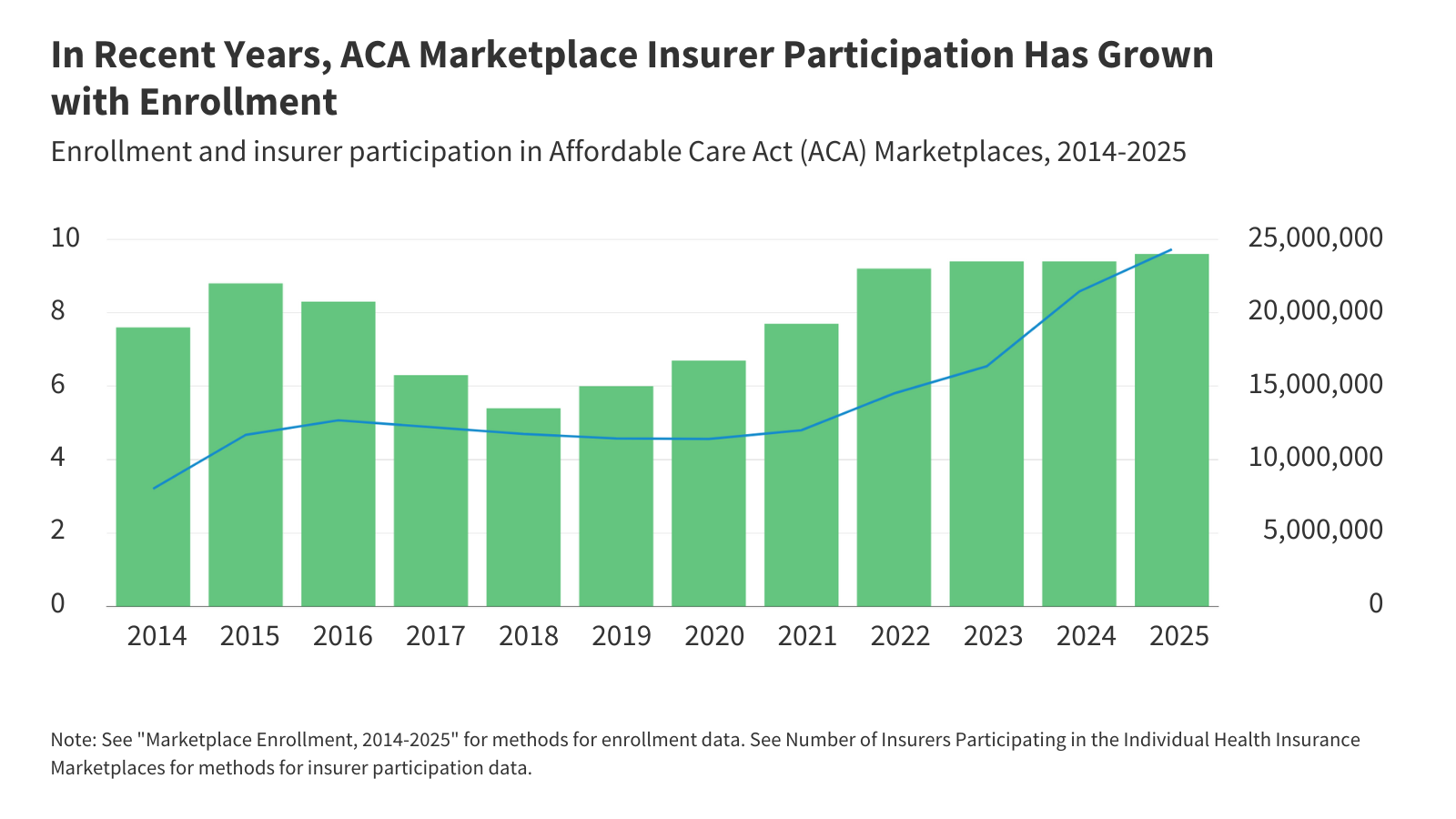
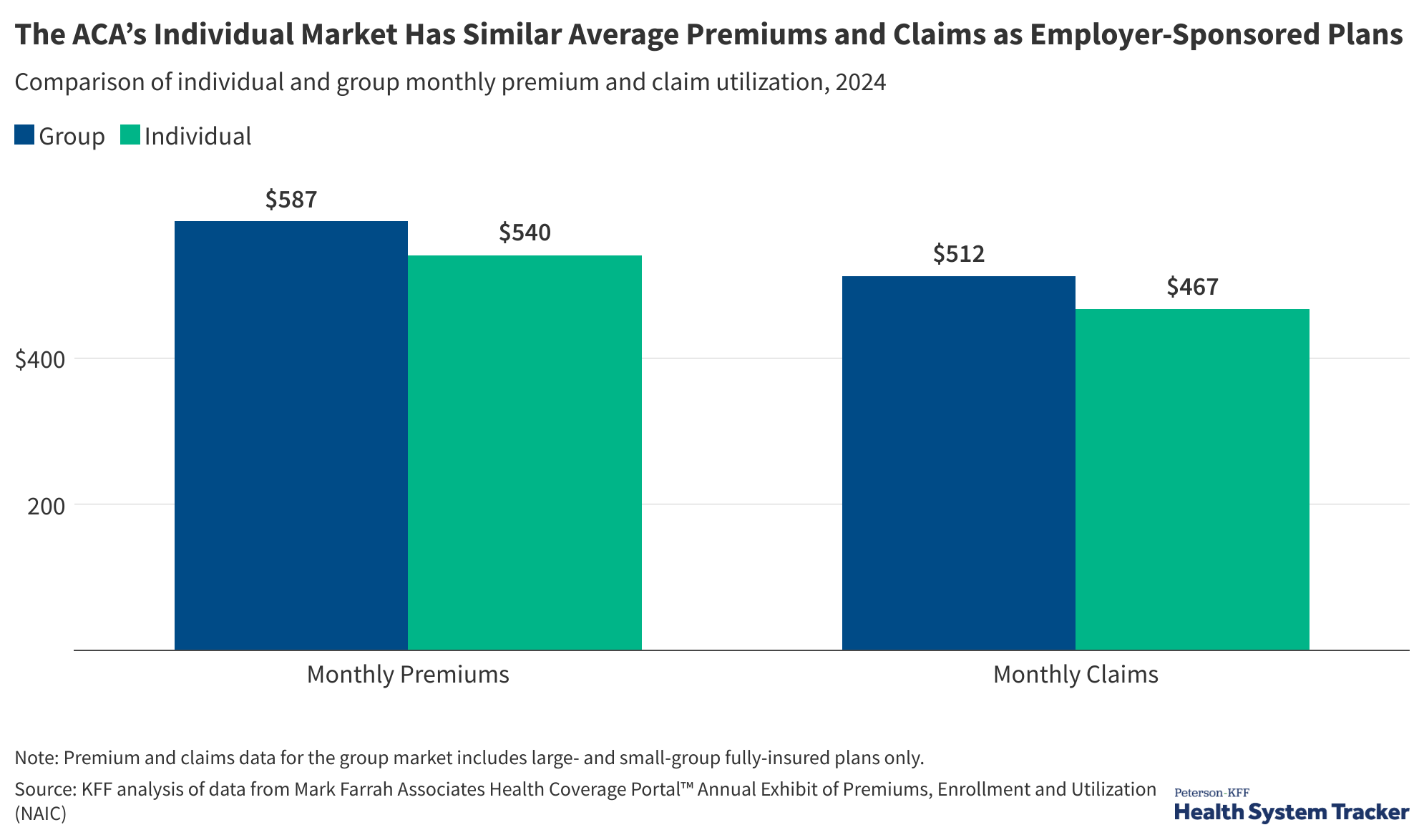
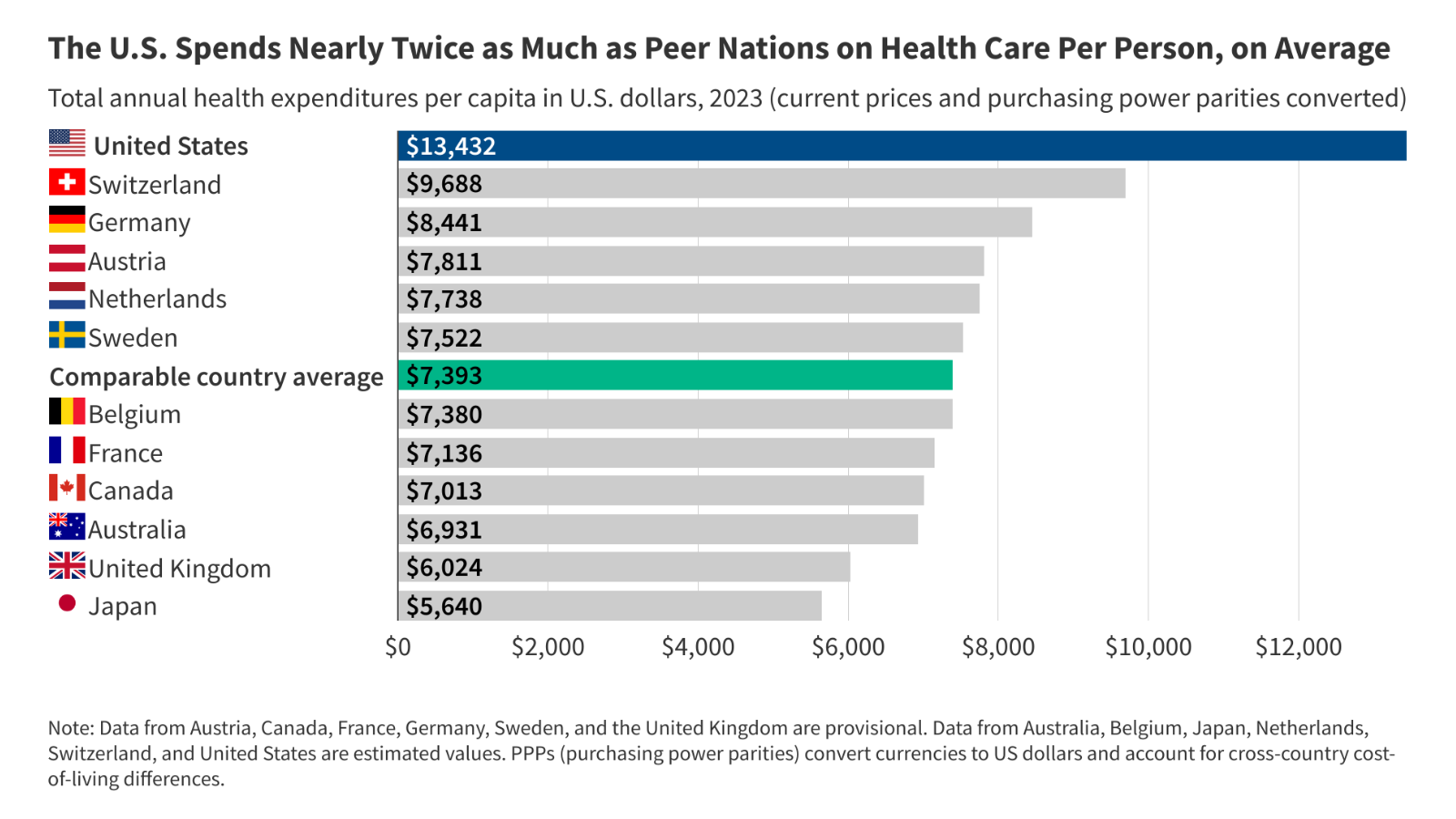
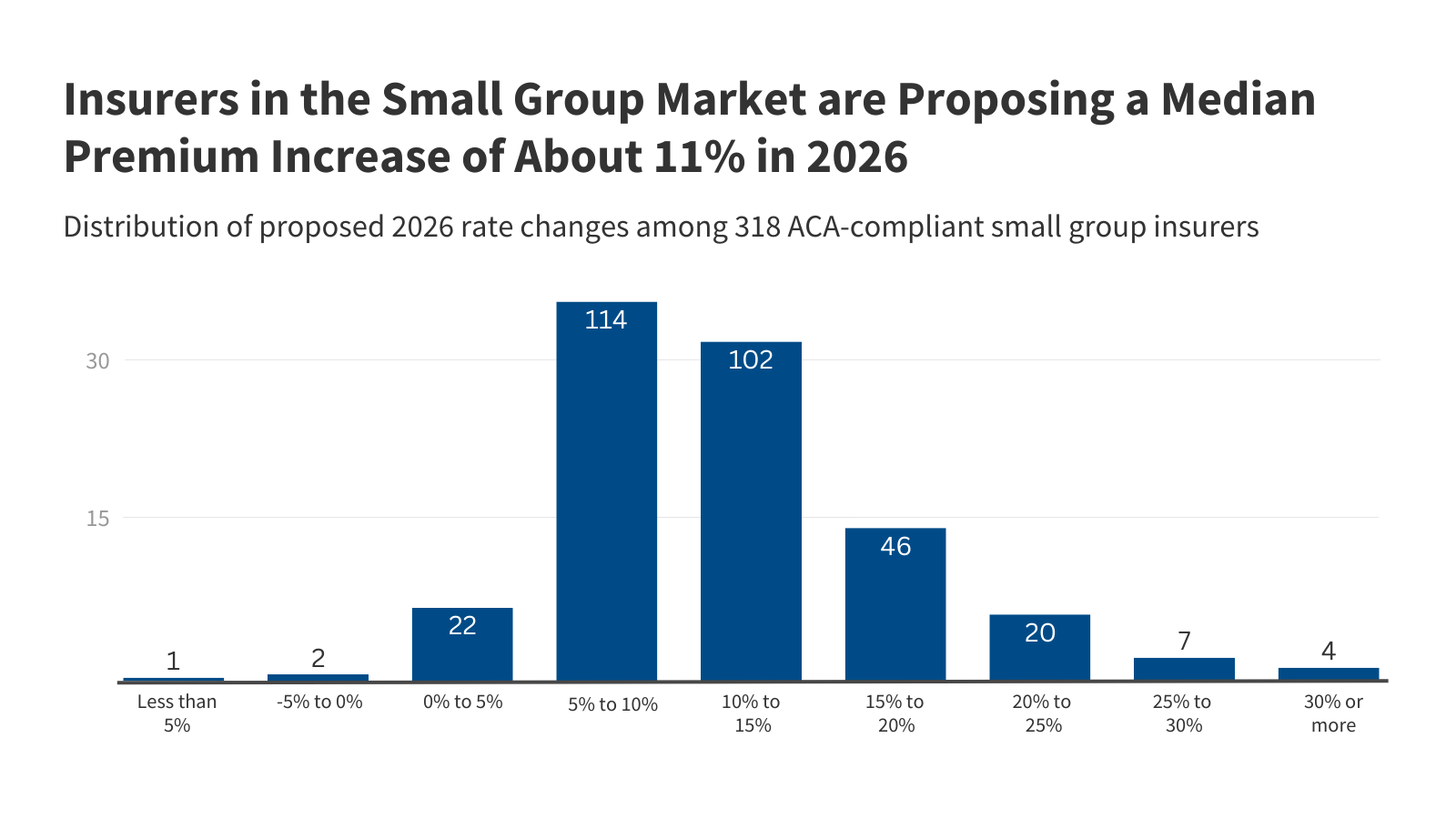
Health Policy in 2026
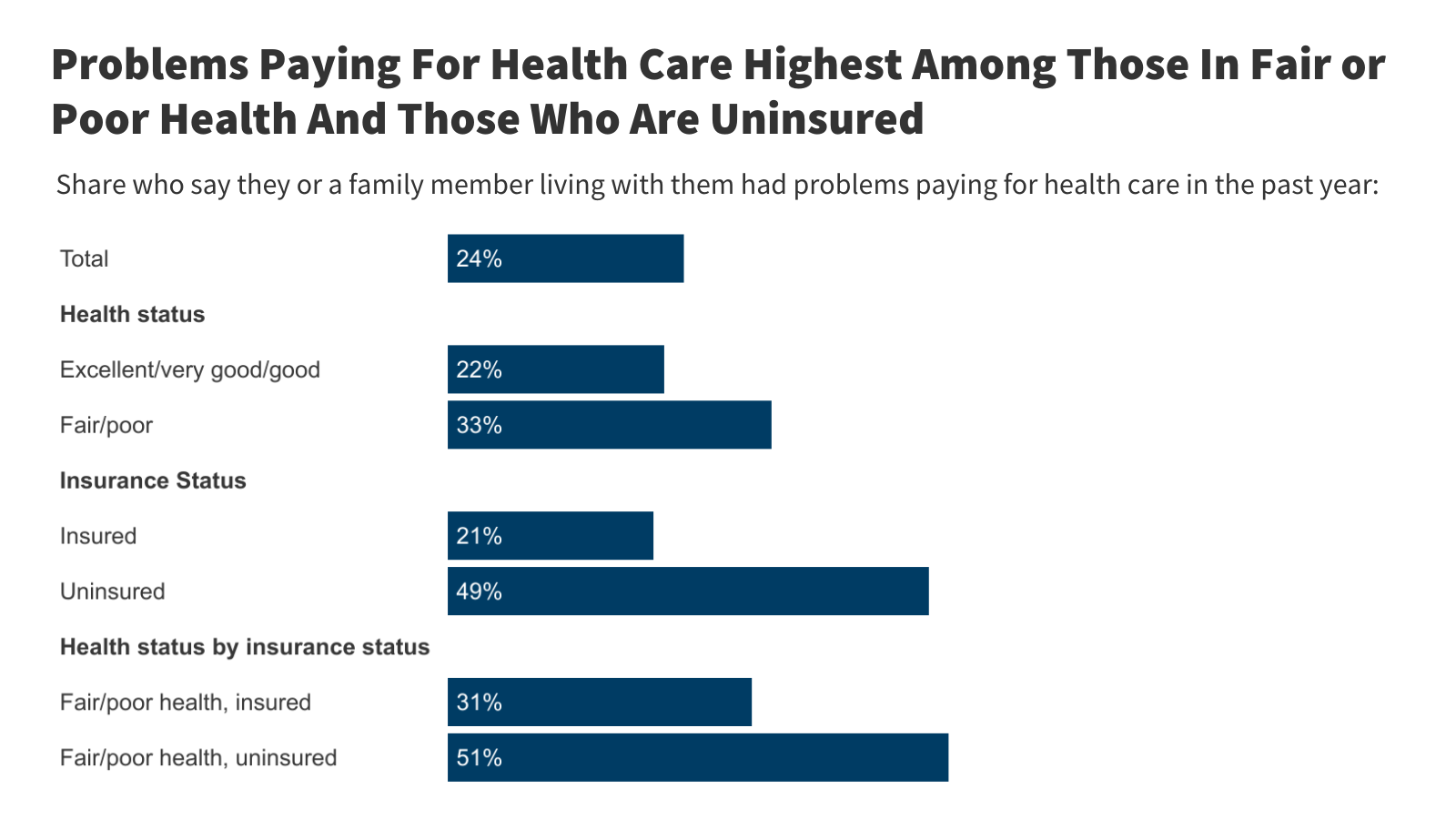
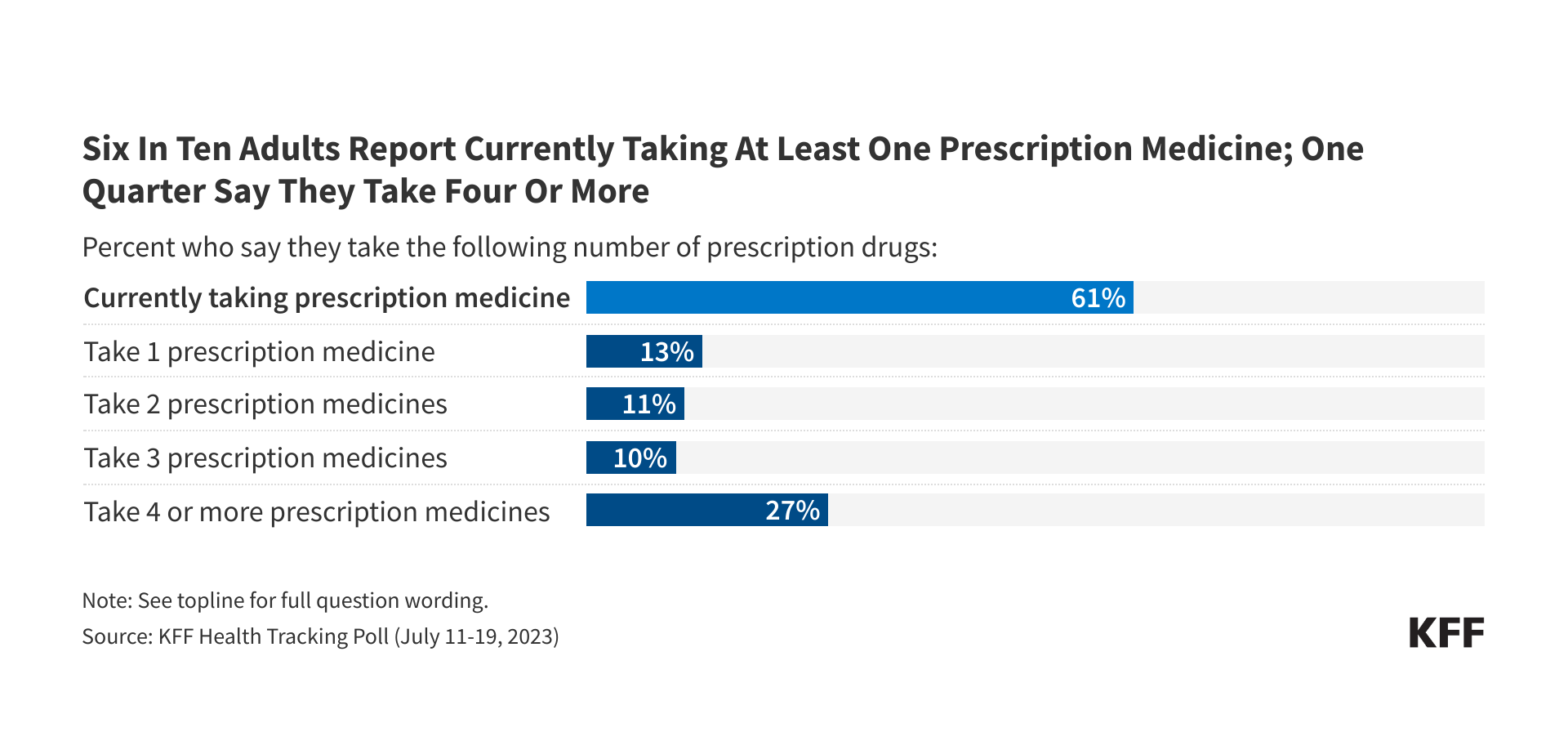
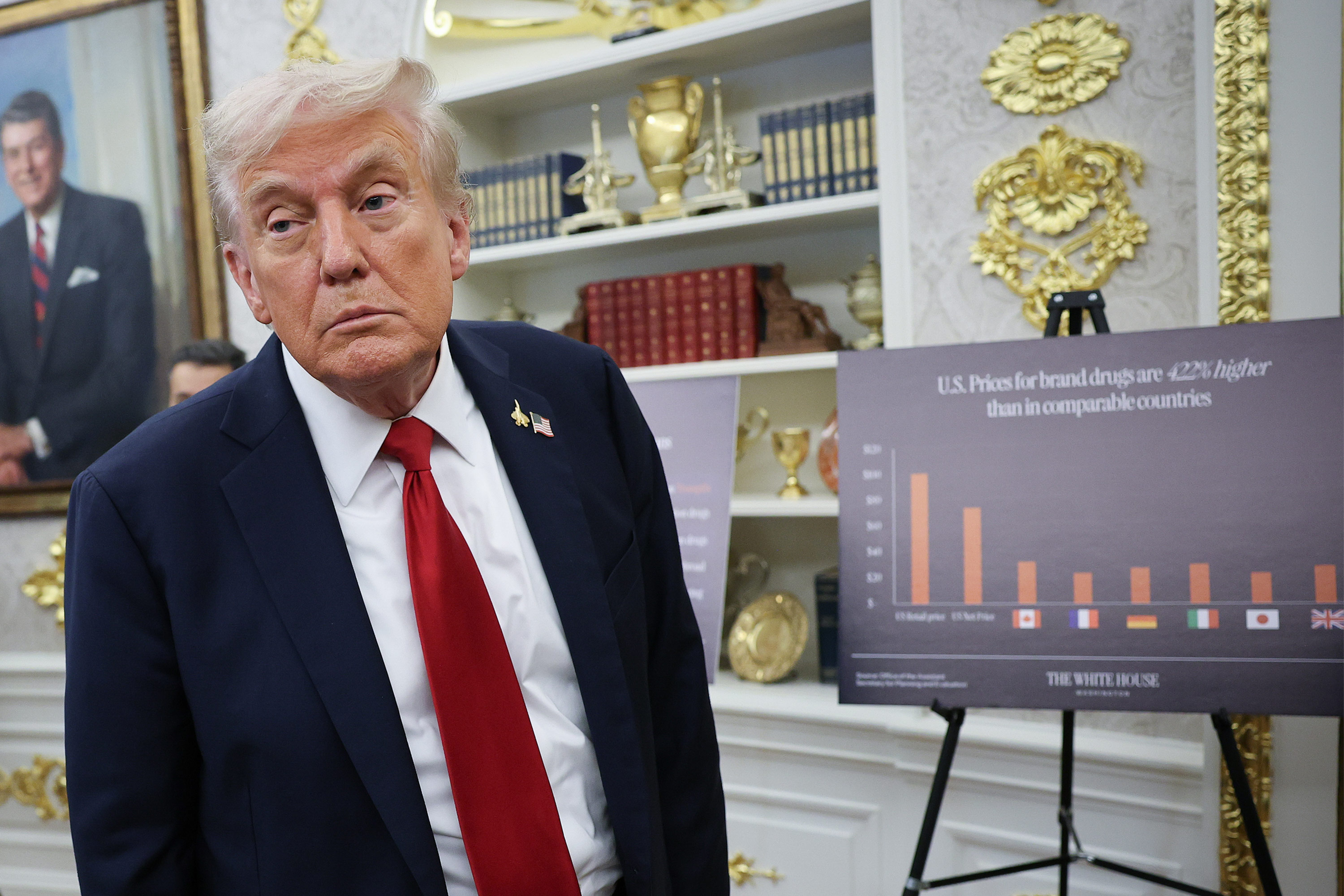
In a new column, President and CEO Dr. Drew Altman forecasts eight things to look for in health policy in 2026. “First and foremost,” he writes, “is the role health care affordability will play in the midterms.” And, he notes: “The average cost of a family policy for employers could approach $30,000 and cost sharing and deductibles will rise again after plateauing for several years.” View all of Drew’s Beyond the Data Columns